Imagine you’re in your kitchen, pouring a glass of freshly purified RO water. It’s crystal clear and pure, but have you ever wondered if it can conduct electricity?
If you’ve ever been curious about the science behind water and electricity, you’re in the right place. You might think that pure water, like that from your RO system, is a poor conductor. But there’s more to the story than meets the eye.
Understanding this concept could change the way you think about everyday actions, like using appliances around water. Dive into this intriguing topic to uncover the truth and satisfy your curiosity. After all, knowledge is power, and this piece of information might just spark your interest in the fascinating world of science. Keep reading to discover whether your RO water is as safe as you think when it comes to conducting electricity.

Credit: www.facebook.com
What Is Ro Water?
Reverse Osmosis (RO) water is purified water obtained through a filtration process. This process removes contaminants, impurities, and dissolved salts from the water. RO systems are widely used in homes and industries to improve water quality. These systems use a semi-permeable membrane to separate unwanted substances from the water.
RO water is often considered cleaner and safer for consumption. It does not contain harmful chemicals or pollutants. This makes it a popular choice for drinking and cooking. People trust RO water for its purity and taste.
What Is Reverse Osmosis?
Reverse Osmosis is a technology used to purify water. It involves forcing water through a membrane. This membrane filters out impurities and contaminants. The result is clean, fresh water.
How Does Ro Water Differ?
RO water is different because it has fewer impurities. It lacks minerals found in regular tap water. This absence can affect taste and nutritional value. RO water is often softer and clearer than regular water.
Can Ro Water Conduct Electricity?
RO water has low conductivity due to fewer ions. It lacks minerals like calcium and magnesium. These minerals help conduct electricity. RO water may conduct electricity poorly compared to tap water.

Credit: www.chegg.com
How Ro Systems Work
Reverse Osmosis (RO) systems are key for clean water. They remove impurities through a detailed process. Understanding how RO systems work helps us grasp their benefits. Let’s explore the filtration process and the role of membranes in these systems.
Filtration Process
The filtration process in RO systems is crucial. It starts with pre-filters. These remove larger particles like dust and rust. The water then moves to the RO membrane. This is where the main filtration happens. The RO membrane removes dissolved salts and contaminants. This step ensures the water is pure and safe.
After the RO membrane, the water goes through post-filters. These enhance the taste and quality. The filtration process is efficient. It ensures that every drop of water is clean and fresh.
Role Of Membranes
Membranes play a vital role in RO systems. They are thin layers made of special material. These membranes allow water molecules to pass through. But they block larger contaminants like chemicals and bacteria.
The membrane’s structure is unique. It acts like a barrier, ensuring only pure water passes. This makes RO systems effective in water purification. Membranes are the heart of the RO process. They ensure the water we drink is safe and clean.
Conductivity Basics
Understanding conductivity helps grasp the basics of electricity. It’s about how materials allow electric current to flow. Pure water doesn’t conduct electricity well. But adding substances changes things. RO water is purified to remove impurities. This process affects its ability to conduct electricity.
What Conducts Electricity?
Materials that allow electric currents are conductors. Metals like copper and aluminum are good conductors. They let electricity pass through easily. Insulators, like rubber, do not conduct electricity. They block the flow of current. This difference is crucial in electrical systems.
Role Of Ions In Conductivity
Ions are charged particles. They play a key role in conductivity. In water, ions like sodium and chloride help conduct electricity. RO water has fewer ions. This makes it less conductive than regular tap water. The purification removes minerals that form ions. Understanding ions helps in studying water conductivity.
Electrical Conductivity Of Ro Water
RO water, or Reverse Osmosis water, is often used for its purity. Many wonder about its ability to conduct electricity. Electrical conductivity depends on dissolved ions. In pure water, ions are few. Let’s explore how RO water measures up.
Purity And Conductivity
RO water is highly purified. It removes most contaminants. This includes minerals that conduct electricity. Fewer minerals mean lower conductivity. Pure water has less conductivity. RO water is almost as pure as distilled water. So, its conductivity is minimal.
Comparison With Tap Water
Tap water contains various minerals and ions. These enhance its conductivity. Common minerals include calcium and magnesium. They help conduct electricity. RO water lacks these minerals. Thus, it conducts electricity poorly. Tap water and RO water differ significantly in this aspect.
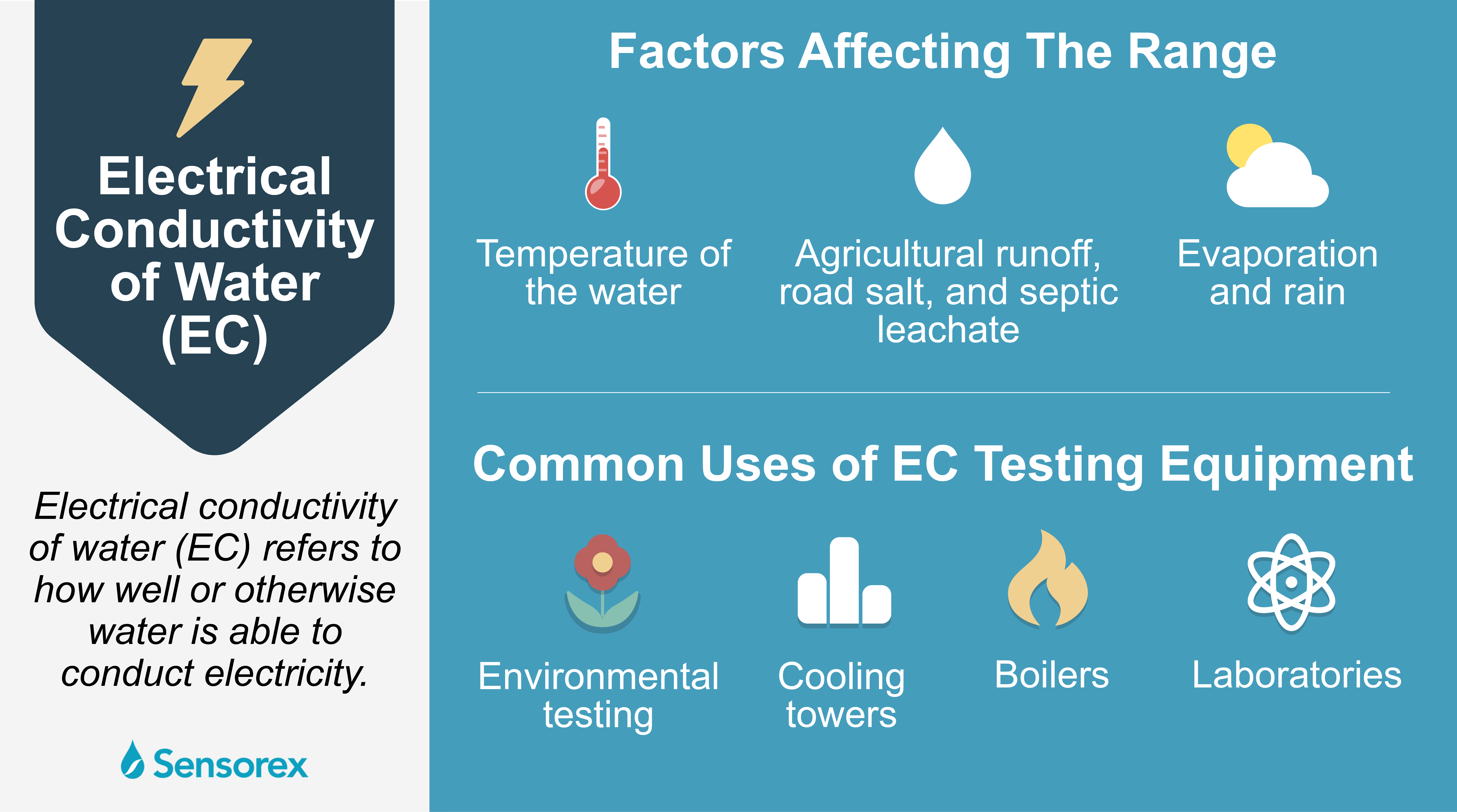
Factors Affecting Conductivity
RO water, lacking impurities, has low conductivity. Pure water doesn’t conduct electricity well. Ions or impurities are needed to carry current.
Factors affecting the conductivity of RO water are crucial for understanding its behavior in electrical applications. RO water, known for its purity, typically exhibits low electrical conductivity. However, several factors can influence this property. Impurities and temperature play significant roles in determining how well RO water can conduct electricity. Let’s delve into these factors to comprehend their impact on RO water conductivity.Presence Of Impurities
Impurities significantly affect RO water conductivity. Even trace amounts of dissolved minerals can increase conductivity. RO systems aim to remove impurities, yet slight amounts may remain. These residual impurities alter the water’s ability to conduct electricity. Conductivity rises as impurity levels increase. Minerals like sodium and calcium are common culprits. They enhance the flow of electrical current through water.Temperature Influence
Temperature changes also impact RO water conductivity. As temperature rises, water molecules move faster. This increased movement allows ions to carry electrical current more effectively. Warm water conducts electricity better than cold water. This is due to the increased mobility of ions in heated conditions. Temperature adjustments can thus modify conductivity levels. Understanding this relationship helps in practical applications of RO water.Practical Implications
RO water, or Reverse Osmosis water, is often used for its purity. But can it conduct electricity? The practical implications of this question are significant. Understanding these can influence various applications and safety measures. RO water generally has very low conductivity due to its lack of ions. This characteristic can be both a benefit and a concern, depending on the situation.
Safety Considerations
RO water has low electrical conductivity. This makes it safer for electrical equipment. It reduces the risk of short circuits. But there is a downside. If RO water contacts electrical systems, it may not trigger safety devices. These devices rely on water’s ability to conduct electricity. Hence, one must exercise caution. Proper safety checks are necessary in these environments.
Applications Of Ro Water
RO water is used in laboratories. Its purity is ideal for experiments. It prevents contamination in chemical processes. Electronics manufacturing also benefits. Clean water avoids mineral buildup on sensitive parts. In the food industry, RO water ensures product purity. It plays a role in maintaining quality control. These applications highlight the value of understanding RO water’s properties.
Misconceptions And Myths
Water is a fascinating element, often surrounded by misconceptions and myths, especially regarding its ability to conduct electricity. You might have heard varying opinions about whether RO (Reverse Osmosis) water can conduct electricity. These beliefs are widespread, but not always accurate. Let’s dive into some common misunderstandings and explore the scientific clarifications that can help you make informed decisions.
Common Misunderstandings
Many people believe that RO water, due to its purity, cannot conduct electricity. It’s easy to see why—pure water lacks the minerals and ions that typically facilitate electrical conductivity. However, this isn’t the full picture.
Another common myth is that RO water is entirely devoid of any electrical properties. You might even have heard the idea that it’s as insulating as distilled water. But, unlike distilled water, RO water can still contain trace amounts of impurities.
Have you ever wondered why your electrical appliances warn against contact with water? It’s because water, in general, is not a perfect insulator. Even RO water can conduct electricity under certain conditions.
Scientific Clarifications
Scientifically speaking, pure water is indeed a poor conductor of electricity. This is because it lacks free ions. RO water removes most impurities, but some ions can remain, allowing it to conduct electricity, albeit weakly.
If you ever test RO water with a conductivity meter, you might be surprised. You’ll find it does conduct electricity, just not as effectively as regular tap water. This is due to the presence of minimal residual ions post-filtration.
But here’s a thought-provoking question: if RO water can conduct electricity, what does that mean for its use in electrical applications? It’s crucial to understand that while RO water is safer than tap water, it should still be kept away from electrical circuits.
Next time you consider the properties of RO water, remember that while it’s purer, it’s not entirely free from conductivity. Educating yourself about these scientific truths can help you avoid the pitfalls of common myths and make smarter, safer choices.
Credit: sensorex.com
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Ro Water Conduct Electricity?
RO water has very low mineral content, making it a poor conductor of electricity. It lacks the ions needed for electrical conductivity, unlike tap water, which contains more minerals. Therefore, RO water is often used in applications where reduced electrical conductivity is desired.
Why Is Ro Water Less Conductive?
RO water undergoes filtration to remove impurities, including minerals and ions. These ions are essential for electrical conductivity. As a result, RO water has a lower conductivity compared to regular water. Its purity makes it suitable for specific applications where minimal conductivity is needed.
Is Distilled Water Similar To Ro Water?
Distilled water and RO water both have reduced mineral content. However, distilled water is produced through evaporation and condensation, while RO water is filtered. Both types have low conductivity, but their production methods differ, affecting their purity levels and applications.
Can Ro Water Be Used In Electrical Appliances?
Yes, RO water can be used in electrical appliances that require low conductivity water. Its reduced mineral content minimizes the risk of electrical malfunctions. However, always follow appliance guidelines to ensure compatibility, as some devices may require specific water types for optimal performance.
Conclusion
Ro water cannot conduct electricity. Its purity prevents electron flow. Contaminants typically enable conductivity in water. This is why pure water is used in electronics. It minimizes risk of electrical conduction. Understanding this helps in safe water use. Especially in homes with electrical appliances nearby.
Always ensure your water source is reliable. This guarantees safety and efficiency. Pure water can be beneficial in many scenarios. But its non-conductive nature is crucial to note. For both safety and practical applications. Stay informed and make smart choices with your water.

Hasan Al Sarker is a Reverse Osmosis Specialist. He has worked for many years to ensure safe drinking water for all. His research paper has been published in several journals, including Issue, Medium, and Slideshare. He is recognized as a water doctor among specialists though he did not attend medical college.
Besides working as a researcher of reverse osmosis technology, he is also very fancy with the kitchen and cooking. His guides are reading thousands of people every day. As a head of content, he is responsible for all the published articles at RO System Reviews.

