Are you tired of dealing with hard water stains on your dishes, dry skin, or dull hair? You’re not alone.
Hard water can cause a lot of everyday problems, but the good news is there’s a simple solution: an ion exchange water softener. But how exactly does this device work to make your water softer and your life easier? You’ll discover the science behind ion exchange water softeners and why they might be the answer to your hard water troubles.
Keep reading to learn how this technology can transform your home water and improve your daily routine.
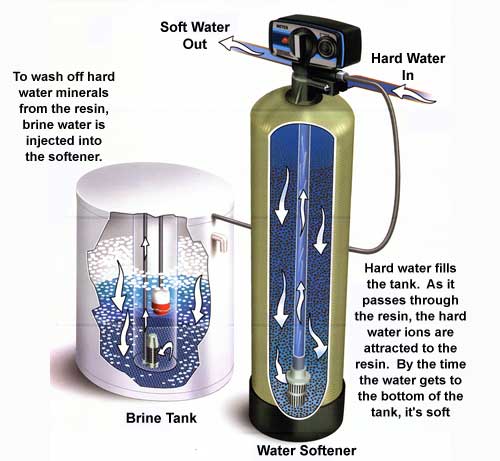
Credit: filtersmart.com
Ion Exchange Basics
Understanding the basics of ion exchange helps explain how water softeners work. This process removes hard minerals from water. It makes water gentler on skin, clothes, and pipes. The ion exchange happens inside the water softener unit. It swaps harmful minerals with safer ones. This simple swap changes hard water into soft water.
Let’s explore the main ideas behind ion exchange. Knowing what happens at the microscopic level clarifies how softening works. This knowledge helps you appreciate your water softener’s role.
What Is Ion Exchange?
Ion exchange is a chemical process. It swaps ions between two substances without changing their structure. In water softening, it means exchanging hard minerals for softer ones. Hard minerals like calcium and magnesium leave the water. They get replaced by sodium or potassium ions. These softer ions do not cause scale or stains. The exchange happens inside a resin bed in the softener. The resin holds sodium or potassium ions ready to swap.
Key Ions In Water Softening
The main ions involved are calcium (Ca²⁺), magnesium (Mg²⁺), sodium (Na⁺), and potassium (K⁺). Calcium and magnesium cause water hardness. They make water leave spots and scale. Sodium and potassium replace these hard ions during ion exchange. The resin beads hold sodium or potassium ions tightly. When hard water passes through, calcium and magnesium attach to the resin. Sodium or potassium ions release into the water. This swap removes hardness and softens the water effectively.
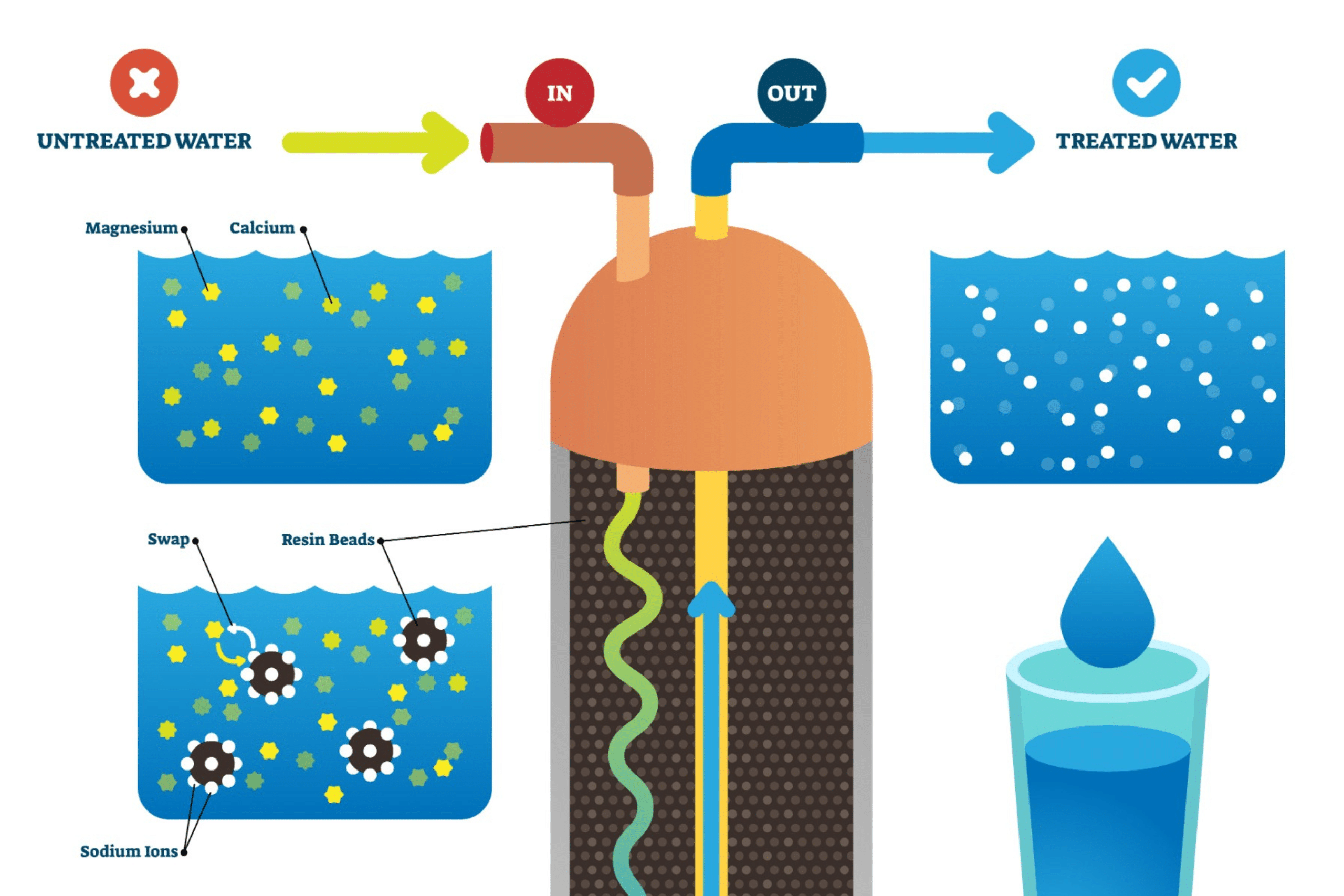
Credit: aquanology.com
How Water Softeners Work
Water softeners remove hard minerals from water. These minerals cause scale and damage pipes. The system uses a special process to clean the water. It makes water better for washing and drinking.
The Role Of Resin Beads
Inside the softener, tiny resin beads are key. They carry a small electric charge. This charge attracts hard minerals like calcium and magnesium. The beads hold these minerals tightly, keeping them out of your water.
Ion Swap Process
Hard minerals swap places with sodium ions on the beads. This swap is called ion exchange. The beads catch the hard minerals and release sodium. Sodium is safe and does not cause hardness. This process cleans water as it passes through the softener.
Regeneration Cycle
Over time, beads fill up with hard minerals. The softener must clean the beads to keep working. It uses a salt solution to wash minerals away. This step is called regeneration. It resets the beads so they can soften water again.
Types Of Ion Exchange Softeners
Ion exchange water softeners come in different types. Each type works in a unique way to reduce hard water problems. Understanding these types helps you choose the right softener for your home or business.
Some softeners use salt to remove minerals. Others use salt-free methods to soften water without chemicals. Both have benefits and fit different needs.
Salt-based Softeners
Salt-based softeners remove hardness by swapping minerals with sodium. Hard water passes through resin beads inside the softener tank. The beads attract calcium and magnesium. These minerals stick to the beads. Sodium ions replace the hard minerals in the water. Soft water flows out, ready for use.
Over time, the beads fill with hardness minerals. The softener regenerates by flushing the beads with a salt brine. This process removes the minerals and recharges the beads. Salt-based softeners are very effective at reducing scale and build-up. They work well for homes with hard water problems.
Salt-free Alternatives
Salt-free softeners do not remove hardness minerals. Instead, they change how minerals behave in water. These systems use special filters or conditioners. They prevent minerals from sticking to pipes and appliances. This reduces scale without adding salt.
Salt-free options are easier to maintain. They do not need salt or regular regeneration. These softeners are good for people with salt restrictions. They also protect the environment by reducing salt discharge. Salt-free systems work best in areas with mild to moderate hardness.
Benefits Of Using Water Softeners
Using a water softener brings many benefits to your home and health. It changes hard water into soft water by removing minerals like calcium and magnesium. Soft water improves daily tasks and protects your plumbing system.
Improved Water Quality
Soft water feels smoother and tastes better than hard water. It stops white spots on dishes and glassware. Soft water also helps soap and detergent work better. This means cleaner clothes and dishes with less effort.
Protecting Appliances
Hard water causes scale build-up inside appliances. This build-up reduces their life and efficiency. Soft water prevents scale in water heaters, dishwashers, and washing machines. Appliances last longer and use less energy with soft water.
Skin And Hair Benefits
Soft water is gentle on skin and hair. It stops dryness and irritation caused by hard water. Bathing with soft water leaves skin feeling soft and smooth. Hair becomes shinier and easier to manage.
Maintenance And Care
Proper maintenance keeps your ion exchange water softener working well. It helps avoid problems and extends the system’s life. Regular care ensures soft water always flows in your home. Simple steps can make a big difference in performance.
When To Refill Salt
Check the salt level in the brine tank monthly. The salt should stay above the water line. Refill the tank when salt drops below half full. Use high-quality salt designed for water softeners. Avoid overfilling to prevent salt bridging and clogs.
Cleaning The System
Clean the brine tank once a year to remove salt buildup. Turn off the system and empty the tank before cleaning. Use warm water and mild soap for scrubbing. Rinse thoroughly to avoid soap residue. Clean the resin bed every few years with a resin cleaner.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Soft water stops? Check salt levels and add if low. Salt bridges can block salt flow; break them gently. If water tastes salty, reduce salt usage or check settings. Resin beads wear out over time; replace them if needed. Follow manufacturer instructions for fixing errors.
Environmental Considerations
Ion exchange water softeners help reduce hard water problems. Yet, their use raises important environmental questions. Understanding these concerns can guide better choices. This section explores key environmental effects of ion exchange softeners.
Salt Discharge Impact
Ion exchange softeners use salt to clean their resin beads. During regeneration, salty water flushes out minerals. This discharge enters household wastewater systems. High salt levels can harm soil and plants. It may also affect aquatic life in nearby water bodies. Wastewater treatment plants struggle to remove excess salt. This can lead to increased salinity in natural waters. Salt discharge is a significant environmental challenge for softeners.
Eco-friendly Options
Newer water softeners aim to reduce salt use. Some models use potassium chloride instead of sodium chloride. Potassium is less harmful to plants and soil. Salt-free water conditioners also exist. They do not remove minerals but prevent scale buildup. These options lower salt discharge and environmental harm. Homeowners can also reduce water waste by choosing efficient systems. Regular maintenance helps systems run better and use less salt.
Choosing The Right Softener
Choosing the right ion exchange water softener is key for good results. The right softener saves money and works well for your home. It depends on your water’s hardness, the size of your household, and your budget. Understanding these helps select the best system for your needs.
Assessing Water Hardness
Start by testing the hardness of your water. Water hardness means the amount of minerals like calcium and magnesium. These minerals cause scale and reduce soap’s effectiveness. Test kits or local water reports can show your water hardness level. Knowing this helps pick a softener with the right capacity.
Sizing Your System
Choose a system size based on your water use and hardness. Larger families need bigger softeners to handle more water. A small unit may not soften all water properly. The system’s capacity shows how many grains of hardness it can remove. Match this to your household’s daily water use for best results.
Budget And Features
Set a budget before choosing a softener. Basic models remove hardness well and cost less. Advanced units offer extra features like digital controls or salt-saving options. Consider which features you need and can afford. A simple, reliable softener often works best for most homes.
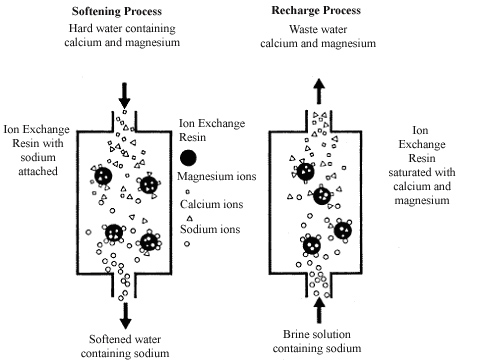
Credit: extensionpublications.unl.edu
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is An Ion Exchange Water Softener?
An ion exchange water softener removes hard minerals like calcium and magnesium. It swaps these minerals with sodium or potassium ions. This process prevents scale buildup and improves water quality. The system uses resin beads that attract and hold hard minerals.
It regenerates regularly to maintain efficiency.
How Does Ion Exchange Remove Hardness From Water?
Ion exchange replaces hardness ions with sodium or potassium ions. Water passes through resin beads that hold sodium ions. Hardness ions stick to the beads and release sodium ions into the water. This exchange softens the water by removing minerals that cause hardness.
How Often Does An Ion Exchange Softener Regenerate?
Regeneration usually happens every few days to weeks, depending on water use. The system flushes out hardness minerals from the resin beads. It then replenishes them with sodium or potassium ions. Proper regeneration ensures continuous soft water and efficient operation.
Can Ion Exchange Water Softeners Remove All Contaminants?
No, ion exchange softeners only remove hardness minerals. They do not eliminate bacteria, viruses, or chemicals. For comprehensive water treatment, additional filtration systems are needed. Softening improves water feel but not overall purity.
Conclusion
An ion exchange water softener removes hard minerals from water. It swaps calcium and magnesium ions with sodium or potassium ions. This process helps prevent scale buildup in pipes and appliances. Soft water feels smoother and cleans better. Regular maintenance keeps the softener working well.
Understanding how it works helps you choose the right system. Clean, soft water improves daily life in many ways. Simple, effective, and reliable—an ion exchange softener benefits your home.

Hasan Al Sarker is a Reverse Osmosis Specialist. He has worked for many years to ensure safe drinking water for all. His research paper has been published in several journals, including Issue, Medium, and Slideshare. He is recognized as a water doctor among specialists though he did not attend medical college.
Besides working as a researcher of reverse osmosis technology, he is also very fancy with the kitchen and cooking. His guides are reading thousands of people every day. As a head of content, he is responsible for all the published articles at RO System Reviews.

