Are you curious about how to make your water cleaner and better for your home? Understanding what an ion exchange filter is can be the key to improving your water quality.
This simple device can remove unwanted minerals and impurities that affect taste, smell, and even your health. By the end of this article, you’ll know exactly how an ion exchange filter works and why it might be the perfect solution for your water needs.
Keep reading to discover how this small filter can make a big difference in your daily life.

Credit: www.coleparmer.com
Ion Exchange Filter Basics
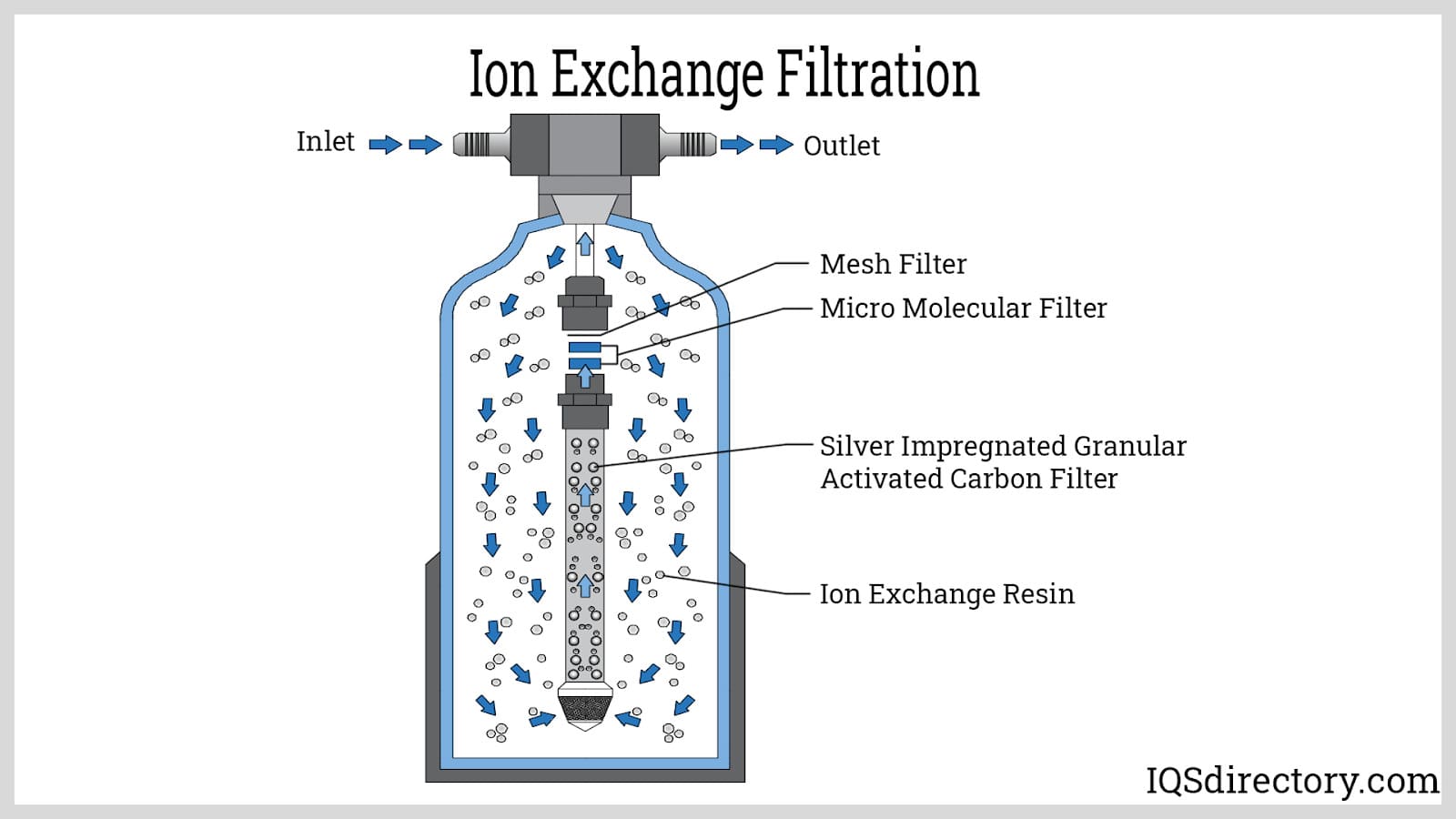
An ion exchange filter is a tool used to clean water by removing unwanted minerals. It helps improve water quality by softening hard water and reducing harmful elements. Understanding how these filters work and the materials they use is important for choosing the right one.
How Ion Exchange Works
Ion exchange works by swapping bad ions in water with good ones. The filter contains resin beads that carry charged particles. As water passes through, harmful ions like calcium and magnesium stick to the beads. In return, the beads release safer ions like sodium or hydrogen. This process changes the water’s chemical makeup, making it cleaner and softer.
Types Of Ion Exchange Filters
There are two main types of ion exchange filters. The first type is a water softener, which removes hardness ions such as calcium and magnesium. The second type targets specific contaminants like heavy metals or nitrates. Some filters combine these types to treat multiple water problems at once. Each type suits different water conditions and needs.
Common Materials Used
Ion exchange filters use special resin beads made from polymers. These beads carry charged groups that attract unwanted ions. Some resins are designed to capture positive ions (cations), while others catch negative ions (anions). The choice of resin depends on the type of impurities in the water. Regular maintenance keeps the resin effective over time.

Credit: shop.culligan.com
Benefits Of Pure Water
Pure water plays a big role in daily life. It affects health, taste, and home appliances. Using an ion exchange filter helps get clean water. This filter removes harmful minerals and makes water better.
Pure water brings many benefits that improve life quality. Below are key advantages of having clean and pure water.
Health Improvements
Pure water reduces harmful minerals like lead and mercury. It lowers risks of health problems. Drinking clean water supports better digestion and skin health. It helps keep the body hydrated and strong.
Taste And Odor Enhancement
Impurities in water cause bad taste and smell. Pure water tastes fresh and clean. It makes cooking and drinking more enjoyable. Removing chlorine and minerals improves water’s natural flavor.
Protection For Appliances
Hard minerals can damage pipes and machines. Pure water prevents scale build-up inside appliances. It helps washing machines, coffee makers, and dishwashers last longer. Clean water lowers maintenance costs and repairs.
Applications Of Ion Exchange Filters
Ion exchange filters have many important uses in different fields. They help remove unwanted ions from water or other solutions. This makes the water cleaner and safer for various purposes. Their ability to exchange ions makes them useful in homes, industries, and labs.
Residential Use
Ion exchange filters improve water quality in homes. They remove hardness caused by calcium and magnesium. This prevents scale buildup in pipes and appliances. Families enjoy softer water for bathing and cleaning. It also protects water heaters and washing machines. These filters make water taste better and safer to drink.
Industrial Applications
Industries use ion exchange filters for many tasks. They treat boiler water to stop scale and corrosion. This saves energy and equipment costs. Factories purify process water to keep products pure. Ion exchange also recovers valuable metals from waste. It helps in chemical manufacturing by controlling water quality.
Laboratory And Medical Uses
Labs rely on ion exchange filters for pure water. This water is essential for experiments and tests. Medical facilities use these filters to prepare dialysis fluids. They ensure water is free from harmful ions. Ion exchange improves the safety and accuracy of lab work.
Maintenance And Longevity
Proper maintenance is key to keeping an ion exchange filter working well. Regular care helps the filter last longer and keeps water quality high. Ignoring maintenance can reduce its effectiveness and cause damage.
Knowing how to care for your filter improves its performance. Simple steps can extend its life and save money on replacements.
Filter Regeneration Process
Ion exchange filters need to regenerate after some use. This process restores their ability to remove unwanted minerals. It usually involves flushing the filter with a salt solution. The salt replaces the collected minerals in the filter. Regeneration keeps the filter clean and effective. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions to regenerate on time.
Signs Of Replacement
Watch for signs the filter needs replacing. Water may taste salty or have a strange odor. The flow rate might slow down significantly. If the filter no longer softens water, it may be worn out. Regular testing helps spot problems early. Replace the filter to maintain good water quality.
Tips For Prolonging Filter Life
Use clean water to reduce debris buildup. Avoid using harsh chemicals near the filter. Check and clean pre-filters regularly. Keep the filter away from extreme temperatures. Regenerate the filter on schedule. These steps help the filter last longer and work better.
Comparing Ion Exchange With Other Filters
Choosing the right water filter depends on your needs. Ion exchange filters work differently than other filters. Understanding these differences helps you pick the best filter for your water quality.
Ion Exchange Vs. Activated Carbon
Ion exchange filters remove hard minerals like calcium and magnesium. Activated carbon filters focus on removing chlorine, bad taste, and odors. Carbon filters do not soften water or remove minerals. Ion exchange changes water hardness by swapping ions. Both filters improve water but target different problems.
Ion Exchange Vs. Reverse Osmosis
Reverse osmosis (RO) filters remove many impurities by pushing water through a fine membrane. Ion exchange only swaps specific ions. RO can remove salts, bacteria, and many chemicals. Ion exchange mainly softens water and removes heavy metals. RO systems need more water and energy than ion exchange units.
Cost And Efficiency Considerations
Ion exchange filters usually cost less than reverse osmosis systems. They also use less water and energy. Activated carbon filters are often the cheapest option. Efficiency depends on water quality and filter maintenance. Ion exchange needs resin replacement over time. Choose a filter that balances cost and cleaning needs.
Environmental Impact
Ion exchange filters help clean water by removing minerals and impurities. This process affects the environment in several ways. Understanding these effects is important for using these filters responsibly. The environmental impact covers waste, sustainability, and alternative solutions.
Waste Management
Ion exchange filters create waste during regeneration. The used resin contains trapped minerals and chemicals. Proper disposal is necessary to avoid pollution. Many places treat this waste as hazardous. Safe handling reduces risks to soil and water. Recycling used resin can lower environmental harm.
Sustainability Practices
Choosing sustainable options helps reduce environmental damage. Using long-lasting resins means fewer replacements. Efficient regeneration uses less water and chemicals. Regular maintenance improves filter life and performance. Some companies follow eco-friendly guidelines for production. Sustainable use supports cleaner water and protects nature.
Eco-friendly Alternatives
Natural filtration methods provide greener options. Activated carbon filters remove impurities without chemicals. Reverse osmosis uses physical barriers instead of resins. Plant-based resins offer biodegradable choices. Combining methods can reduce environmental footprint. Exploring alternatives supports a healthier planet.
Credit: www.iqsdirectory.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Does An Ion Exchange Filter Do?
An ion exchange filter removes unwanted minerals from water by swapping harmful ions with beneficial ones. It softens water and improves taste, making it safer for drinking and household use.
How Does An Ion Exchange Filter Work?
It works by exchanging ions in water with ions from a resin inside the filter. Hard minerals like calcium and magnesium are replaced with sodium or potassium ions, reducing water hardness.
What Are The Benefits Of Using An Ion Exchange Filter?
Benefits include softer water, reduced scale buildup, better soap efficiency, and improved appliance lifespan. It also helps prevent plumbing damage caused by hard water minerals.
Where Are Ion Exchange Filters Commonly Used?
They are used in homes, industries, and water treatment plants. Common applications include water softening, wastewater treatment, and chemical purification processes.
Conclusion
An ion exchange filter helps remove unwanted minerals from water. It makes water softer and better for daily use. These filters work by swapping bad ions with good ones. They are easy to use and maintain. Many homes and businesses trust this method for clean water.
Choosing the right filter can improve water quality quickly. Clean water means healthier life and appliances. Understanding how ion exchange filters work helps make smart choices. Simple, effective, and reliable—these filters serve many needs well.

Hasan Al Sarker is a Reverse Osmosis Specialist. He has worked for many years to ensure safe drinking water for all. His research paper has been published in several journals, including Issue, Medium, and Slideshare. He is recognized as a water doctor among specialists though he did not attend medical college.
Besides working as a researcher of reverse osmosis technology, he is also very fancy with the kitchen and cooking. His guides are reading thousands of people every day. As a head of content, he is responsible for all the published articles at RO System Reviews.

