Have you ever noticed white spots on your dishes or your soap not lathering well? That’s often a sign of hard water.
But how does your water softener actually fix this problem? The secret lies in a clever process called ion exchange. Understanding how ion exchange works can help you appreciate how your water softener protects your pipes, appliances, and skin. Keep reading, and you’ll discover how this simple yet powerful method transforms hard water into soft, clean water for your home.
Basics Of Ion Exchange
Understanding the basics of ion exchange is key to grasping how water softening works. Ion exchange is a chemical process that removes unwanted minerals from hard water. This process helps protect pipes, appliances, and improves water quality. The heart of this system lies in special materials called resins. These resins swap hard minerals with softer ones, making water gentler and safer for daily use.
What Is Ion Exchange
Ion exchange is a process where ions are swapped between a solution and a solid material. In water softening, it removes calcium and magnesium ions. These ions cause hardness and build-up in pipes and appliances. The resins in the system hold sodium or potassium ions. When hard water passes through, the resins release sodium or potassium. At the same time, they capture calcium and magnesium ions. This exchange softens the water effectively and continuously.
Types Of Ion Exchange Resins
Two main types of ion exchange resins exist for water softening. Cation exchange resins are the most common. They replace positive ions like calcium and magnesium with sodium or potassium. Anion exchange resins work differently. They remove negative ions such as chloride or sulfate. Most water softeners use cation resins because hard water problems come from positive ions. Resins come in bead form, allowing water to flow easily through them. The quality and type of resin affect the softening efficiency and lifespan of the system.
Credit: filtersmart.com
Hard Water And Its Effects
Hard water contains high levels of certain minerals. These minerals cause problems in homes and industries. They affect water quality and daily tasks. Understanding hard water helps in choosing the right treatment.
Hard water can make cleaning harder and damage appliances. It also affects plumbing systems and water heaters. Knowing the causes and effects of hard water is important for maintenance.
Minerals Causing Hardness
Calcium and magnesium are the main minerals in hard water. They come from rocks and soil. These minerals dissolve in water as it moves through the ground. Other minerals like iron can also add to hardness.
Calcium makes water “hard” by forming scale deposits. Magnesium has similar effects and can cause soap to form scum. These minerals change how water behaves in homes and businesses.
Impact On Plumbing And Appliances
Hard water leaves deposits inside pipes and fixtures. These deposits build up over time and reduce water flow. Blocked pipes increase the risk of leaks and damage.
Appliances like water heaters and dishwashers get coated with mineral scale. This coating lowers their efficiency and shortens lifespan. Hard water also causes stains on dishes, clothes, and sinks.
Using water softening methods can protect plumbing and appliances. It helps save money on repairs and energy costs. Soft water improves cleaning and extends appliance life.
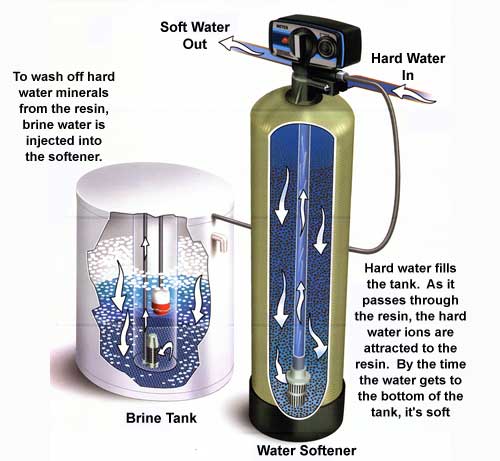
Ion Exchange Process In Water Softening
The ion exchange process is the heart of water softening. It changes hard water into soft water by removing minerals that cause hardness. This process uses special materials called resins. These resins catch hard minerals and swap them with softer ones.
The process runs inside a water softener tank. Hard water flows through the tank. The resins inside work to clean out calcium and magnesium. Soft water comes out, ready for use in your home.
How Resins Remove Hardness
Resins are tiny beads with a negative charge. Hard minerals like calcium and magnesium have a positive charge. The resins attract and hold these minerals. They keep the hardness in the tank and stop it from reaching your taps.
Over time, the resins fill up with hard minerals. They need to be cleaned to work well again. This cleaning is called regeneration. It clears the minerals and resets the resins.
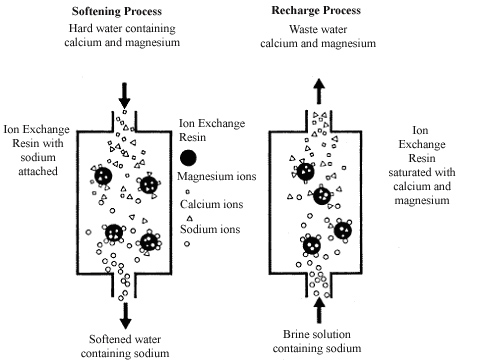
Role Of Sodium And Calcium Ions
Sodium ions are the key to regeneration. They come from salt added to the softener. During regeneration, sodium ions replace the calcium and magnesium on the resin. This frees the resin to catch more hard minerals.
Calcium and magnesium ions leave the resin and wash away. The softener then works like new. This cycle keeps water soft and safe for your home.
Regeneration Of Ion Exchange Resins
Ion exchange resins are at the heart of water softening systems. Over time, these resins collect hard minerals like calcium and magnesium. This process stops the resin from working well. Regeneration restores the resin’s ability to soften water. It is a key part of keeping the system effective and efficient.
Why Regeneration Is Needed
Resins trap hard minerals from water. After a while, the resin becomes full. It cannot hold any more minerals. At this point, the water softener stops working properly. Regeneration clears out the trapped minerals. It recharges the resin with sodium or potassium ions. This makes the resin ready to soften water again.
Steps In The Regeneration Cycle
The regeneration cycle has several steps. First, the resin tank is flushed with brine solution. The salt in the brine replaces the hard minerals on the resin. Next, the minerals and brine are washed away and drained. Then, clean water rinses the resin to remove any leftover brine. Finally, the resin is ready to soften water once more. This cycle repeats regularly to maintain water softness.
Types Of Water Softeners Using Ion Exchange
Ion exchange is a common method to soften water by removing hard minerals. Different water softeners use this process but vary in design and materials. Understanding these types helps choose the right softener for your needs.
Salt-based Softeners
Salt-based softeners use resin beads to trap hard minerals like calcium and magnesium. These beads exchange the minerals with sodium ions from salt. The system needs regular salt refills to keep working well. This type effectively lowers water hardness and prevents scale buildup.
It works automatically by passing water through the resin tank. Hard minerals stick to the beads, and soft water flows out. Periodically, the system cleans the beads using a saltwater solution. This process restores the beads’ ability to soften water.
Salt-free Alternatives
Salt-free softeners use a different approach but still rely on ion exchange principles. They condition water without adding sodium. Instead, they change how minerals behave to stop scale formation.
This option suits people avoiding extra salt in water. It requires less maintenance and does not need salt refills. While it does not remove hardness minerals, it reduces their negative effects on pipes and appliances.
Benefits Of Ion Exchange Softeners
Ion exchange softeners offer several key benefits that improve daily water use. They effectively remove hard minerals from water, making it softer and safer for home use. These systems help protect plumbing and appliances, extending their life and efficiency. Understanding these benefits shows why ion exchange softeners are a smart choice.
Improved Water Quality
Ion exchange softeners remove calcium and magnesium from water. These minerals cause hardness and build-up in pipes. Softer water feels better on skin and hair. It also helps soap and detergents work better. The result is cleaner dishes, clothes, and surfaces. Drinking softened water can taste better too.
Protection For Appliances
Hard water can damage appliances like water heaters and dishwashers. Mineral deposits reduce their efficiency and cause breakdowns. Ion exchange softeners prevent these deposits from forming. Appliances last longer and use less energy. This saves money on repairs and utility bills. Softened water keeps your home running smoothly.
Maintenance Tips For Ion Exchange Systems
Maintaining an ion exchange system is key to keeping water softeners working well. Regular care helps the system last longer and keeps water soft. Simple steps can prevent common problems and improve performance. Pay attention to the resin and know when to act.
Monitoring Resin Life
The resin inside the system traps hard minerals from water. Over time, the resin wears out and loses its ability to soften water. Watch for signs like hard water stains or changes in water taste. Test the water hardness regularly to check resin effectiveness. Keep track of how long the resin has been in use. This helps plan for replacement before problems start.
When To Recharge Or Replace
Recharging the resin means cleaning it with salt to restore its softening power. Do this when water hardness rises or after a set period. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for salt use and recharge timing. Replace the resin if recharging no longer fixes the problem. A worn resin cannot soften water well, even after recharging. Replacing it ensures clean, soft water every day.

Credit: medium.com
Environmental Considerations
Ion exchange is a common method to soften water. It removes calcium and magnesium, which cause hardness. This process helps protect pipes and improves soap efficiency. Yet, it brings some environmental concerns. Understanding these issues helps us make better choices.
Salt Usage And Disposal
Ion exchange uses salt to recharge the resin beads. This salt often comes in large amounts. The salty water, called brine, is flushed out during regeneration. This brine can harm soil and water sources. High salt levels affect plant growth and aquatic life. Proper disposal is necessary to reduce damage. Some areas have rules to limit salt discharge. Checking local regulations is important for safe use.
Eco-friendly Alternatives
Alternatives to salt-based softeners are gaining attention. Potassium chloride is one option. It is less harmful to the environment than sodium chloride. Another method is using template-assisted crystallization. This technology changes hardness minerals without salt. Magnetic and electronic water conditioners also exist. These options reduce salt use and pollution. Choosing eco-friendly solutions supports cleaner water and soil.
Credit: extensionpublications.unl.edu
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Ion Exchange In Water Softening?
Ion exchange is a process that removes hardness ions like calcium and magnesium from water. It replaces them with sodium or potassium ions, making water soft and preventing scale buildup in pipes and appliances.
How Does Ion Exchange Resin Work?
Ion exchange resin contains tiny beads that attract and hold hardness ions. When hard water passes through, calcium and magnesium swap places with sodium or potassium ions on the resin beads, softening the water effectively.
Why Is Ion Exchange Important For Water Softening?
Ion exchange prevents scale buildup in plumbing and appliances. It improves water quality, protects household systems, and enhances soap efficiency. This process extends the lifespan of appliances and reduces energy costs.
How Often Should Ion Exchange Resin Be Regenerated?
Ion exchange resin needs regeneration when it becomes saturated with hardness ions. Typically, this occurs every few days to weeks, depending on water hardness and usage. Regeneration uses a salt solution to recharge the resin beads.
Conclusion
Ion exchange removes hard minerals from water effectively. It swaps calcium and magnesium with sodium or potassium ions. This process prevents scale buildup in pipes and appliances. Soft water feels better on skin and hair. It also helps detergents work better during washing.
Regular maintenance keeps the system working well. Understanding ion exchange helps you choose the right water softener. Clean, soft water improves daily life and protects your home. Simple, yet powerful—this method improves water quality every day.

Hasan Al Sarker is a Reverse Osmosis Specialist. He has worked for many years to ensure safe drinking water for all. His research paper has been published in several journals, including Issue, Medium, and Slideshare. He is recognized as a water doctor among specialists though he did not attend medical college.
Besides working as a researcher of reverse osmosis technology, he is also very fancy with the kitchen and cooking. His guides are reading thousands of people every day. As a head of content, he is responsible for all the published articles at RO System Reviews.

