Have you ever wondered how your water gets purified to remove unwanted minerals and chemicals? Understanding ion exchange in water treatment could change the way you see your tap water.
This simple yet powerful process helps make your water cleaner, safer, and better tasting. You’ll discover exactly what ion exchange is, how it works, and why it matters for your health and home. Keep reading to unlock the secrets behind this essential water treatment method and find out how it can benefit you every day.
Ion Exchange Basics
Ion exchange is a common method used to clean water. It helps remove unwanted minerals and impurities. This process improves water quality for drinking, cooking, and industrial use.
The method uses special materials called resins. These resins swap harmful ions in water with safer ones. This basic idea makes ion exchange an effective water treatment option.
How Ion Exchange Works
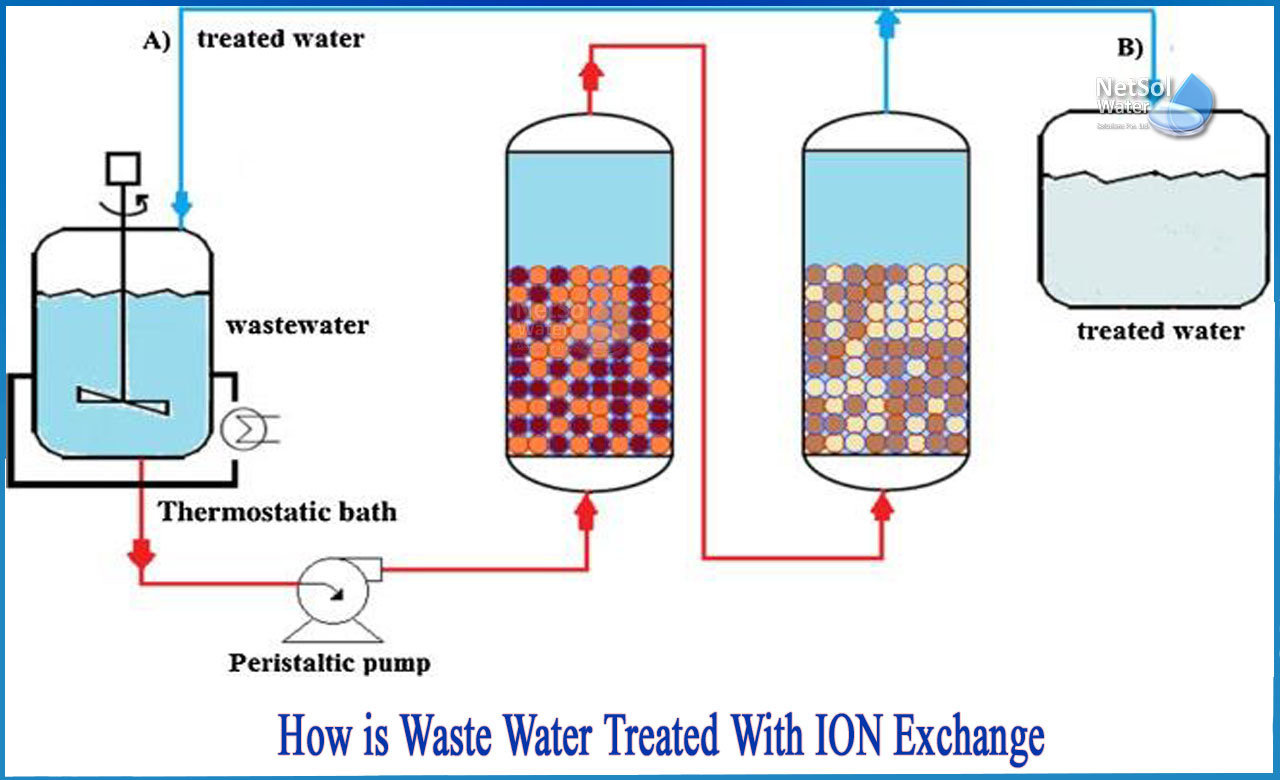
Ion exchange happens inside a tank filled with resin beads. Water flows through these beads. The resin beads hold charged particles called ions.
As water passes, harmful ions stick to the resin. At the same time, the resin releases safe ions into the water. This swap cleans the water by removing bad substances.
Types Of Ion Exchange Resins
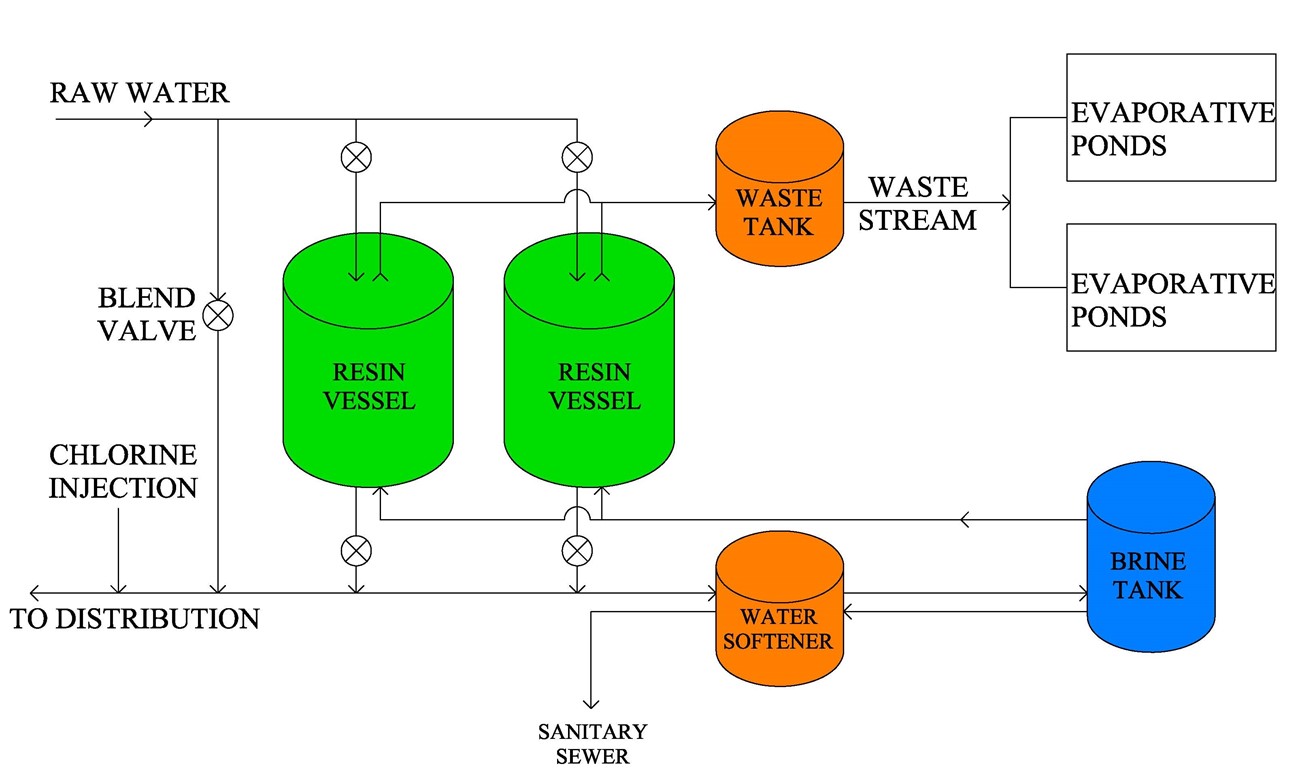
Two main types of resins exist: cation and anion resins. Cation resins remove positive ions like calcium and magnesium. These cause water hardness.
Anion resins remove negative ions like nitrate and sulfate. Each resin targets specific contaminants. Sometimes, both types work together for better cleaning.
Applications In Water Treatment
Ion exchange plays a key role in water treatment. It helps improve water quality by removing unwanted minerals and chemicals. This process is widely used in homes, industries, and water plants. Ion exchange makes water safer and better for different uses.
Softening Hard Water
Hard water contains calcium and magnesium ions. These minerals cause scale buildup in pipes and appliances. Ion exchange replaces calcium and magnesium with sodium ions. This softens the water and prevents damage. Soft water also improves soap efficiency and protects skin.
Removing Contaminants
Ion exchange removes harmful contaminants like lead, arsenic, and nitrate. It traps these ions in the resin beads and cleans the water. This process helps produce safe drinking water. It also protects health by lowering toxic elements in water sources.
Deionization And Demineralization
Deionization removes all charged ions from water. Demineralization is similar but focuses on minerals only. Ion exchange resins capture both positive and negative ions. The result is pure water with very low mineral content. This water is ideal for laboratories, electronics, and power plants.
Benefits Of Ion Exchange
Ion exchange is a popular method used in water treatment to improve water quality. It removes unwanted minerals and contaminants. This process offers many benefits that make it a preferred choice for homes and industries.
Improved Water Quality
Ion exchange softens hard water by removing calcium and magnesium. It also eliminates harmful metals like lead and mercury. This results in cleaner, safer water for drinking and cooking. The water tastes better and is healthier for skin and hair. Appliances last longer because scale build-up decreases.
Cost Efficiency
Ion exchange systems use reusable resins that reduce waste. These systems lower the need for bottled water or chemical treatments. They help save money on plumbing repairs by preventing pipe damage. The process requires little energy, which cuts utility bills. Maintenance is simple and does not cost much.
Environmental Impact
Ion exchange reduces the use of harmful chemicals in water treatment. It produces less wastewater compared to other methods. This helps protect rivers and lakes from pollution. The resin beads used can be regenerated and reused many times. Choosing ion exchange supports a cleaner and greener planet.
Credit: www.netsolwater.com
Maintenance And Challenges
Ion exchange systems need regular care to work well over time. Maintenance helps keep water clean and the system efficient. Challenges can arise from resin wear, fouling, or improper handling. Understanding key tasks and common problems helps avoid costly repairs and downtime.
Resin Regeneration Process
The resin inside ion exchange units traps unwanted ions from water. Over time, the resin becomes full and loses its ability to clean. Regeneration restores its capacity by washing it with a special chemical solution. This solution removes trapped ions and recharges the resin. The process must follow precise steps to ensure full cleaning. Proper timing and chemical use extend resin life and system performance.
Common Issues And Solutions
Resin fouling happens when dirt or iron builds up, reducing efficiency. Regular cleaning or backwashing helps prevent this. Hard water can cause scaling on the resin, blocking ion exchange. Using softening agents or pre-filters reduces scaling. Resin breakdown leads to poor water quality and needs replacement. Check for leaks and pressure drops to find system problems early. Routine inspections and maintenance keep the system running smoothly.
Future Trends
The future of ion exchange in water treatment holds many exciting possibilities. Advances in technology and new approaches aim to improve efficiency and reduce costs. Innovations focus on making the process more sustainable and easier to manage.
These trends show how ion exchange can meet growing water quality challenges. They support cleaner water for homes, industries, and the environment.
Advancements In Resin Technology
Resins play a key role in ion exchange systems. New resins are more selective, targeting specific contaminants better. They last longer and need less frequent replacement. This reduces waste and lowers operating costs. Scientists are developing resins that work in tougher water conditions. These improvements help treat a wider range of water sources.
Integration With Other Treatment Methods
Combining ion exchange with other water treatments improves results. For example, using membranes or filtration alongside ion exchange can remove more impurities. This layered approach increases water purity and system efficiency. It also allows treatment of complex water types. Integration offers flexible solutions for different water needs.
Credit: ebhengineering.com

Credit: eaiwater.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Ion Exchange In Water Treatment?
Ion exchange is a water purification process that removes unwanted ions. It replaces harmful ions with beneficial ones using resin beads. This method effectively softens water and eliminates contaminants like heavy metals and nitrates.
How Does Ion Exchange Remove Hardness From Water?
Ion exchange softens water by replacing calcium and magnesium ions. These hardness-causing ions swap places with sodium or potassium ions on resin beads. This process prevents scale buildup and improves water quality for household use.
What Are Common Applications Of Ion Exchange In Water Treatment?
Ion exchange is used in drinking water purification, wastewater treatment, and industrial processes. It removes hardness, heavy metals, and nitrates. This method also recovers valuable metals and treats boiler feedwater efficiently.
What Types Of Resins Are Used In Ion Exchange?
Cation and anion resins are commonly used in ion exchange. Cation resins remove positive ions like calcium, while anion resins target negative ions like nitrates. Both types help achieve clean, safe water.
Conclusion
Ion exchange helps remove unwanted minerals from water. It improves water quality and taste. This process is common in homes and industries. It works by swapping harmful ions with safe ones. Regular use keeps water clean and healthy. Understanding ion exchange makes water treatment clearer.
Clean water supports better health and daily life. Simple, effective, and widely used—ion exchange matters.

Hasan Al Sarker is a Reverse Osmosis Specialist. He has worked for many years to ensure safe drinking water for all. His research paper has been published in several journals, including Issue, Medium, and Slideshare. He is recognized as a water doctor among specialists though he did not attend medical college.
Besides working as a researcher of reverse osmosis technology, he is also very fancy with the kitchen and cooking. His guides are reading thousands of people every day. As a head of content, he is responsible for all the published articles at RO System Reviews.

