Have you ever wondered how water softeners or purifiers actually clean your water? The secret often lies in something called ion exchange resins.
These tiny beads work quietly behind the scenes to remove unwanted minerals and impurities from your water. Understanding how ion exchange resins work can help you make smarter choices for your home, health, and even your appliances. Stick with me, and I’ll break down the process in simple terms so you can see exactly why these resins are so powerful—and why they might be the solution you’ve been looking for.
Basics Of Ion Exchange Resins
Ion exchange resins are small beads that help clean and soften water. They work by swapping unwanted ions in water with useful ones. This process changes the water’s composition without adding harmful chemicals.
These resins play a key role in water treatment, medicine, and industry. Understanding their basics helps explain how they improve water quality and other materials.
Types Of Ion Exchange Resins
There are two main types of ion exchange resins: cation and anion resins. Cation resins replace positive ions like calcium and magnesium. Anion resins swap out negative ions such as chloride and sulfate.
Some resins are strong acid or base types, while others are weak. Each type suits different water treatment needs and chemical processes.
Chemical Structure And Properties
Ion exchange resins are made of a polymer matrix with charged groups attached. These charged groups attract ions from water. The resin beads are porous, allowing water to flow through easily.
The structure makes resins durable and reusable. They can hold many ions and release them when needed. This ability depends on the resin’s chemical makeup and physical design.

Credit: mytapscore.com
Mechanism Of Ion Exchange
The mechanism of ion exchange is a key process in water purification and chemical separation. It involves swapping ions between a solution and solid resin beads. These resins hold charged particles that attract opposite ions from the liquid. The process cleans or softens the water by removing unwanted ions and replacing them with useful ones.
Ion Attraction And Replacement
Ion exchange resins contain charged sites that attract ions of opposite charge. For example, a resin with negative charges attracts positive ions like calcium or sodium. When water passes through, these ions stick to the resin. At the same time, the resin releases other ions it holds. This swap, or exchange, happens continuously as water flows.
This process removes harmful ions and replaces them with safer ones. It is a physical and chemical reaction. The resin does not dissolve but holds the ions firmly on its surface. This makes ion exchange a reusable and efficient method.
Selectivity And Capacity
Each ion exchange resin has a preference for certain ions. This is called selectivity. Some resins prefer calcium ions more than sodium ions. This selectivity depends on the resin’s chemical structure and the size of ions.
Capacity refers to how many ions a resin can hold before it needs cleaning. A resin with high capacity lasts longer and treats more water. The resin’s capacity depends on its surface area and the number of charged sites.
Applications In Water Purification
Ion exchange resins play a key role in water purification. They help improve water quality by removing unwanted substances. These resins work by exchanging harmful ions in water with safer ones. This process makes water cleaner and safer for use. Below are some important ways ion exchange resins help in water purification.
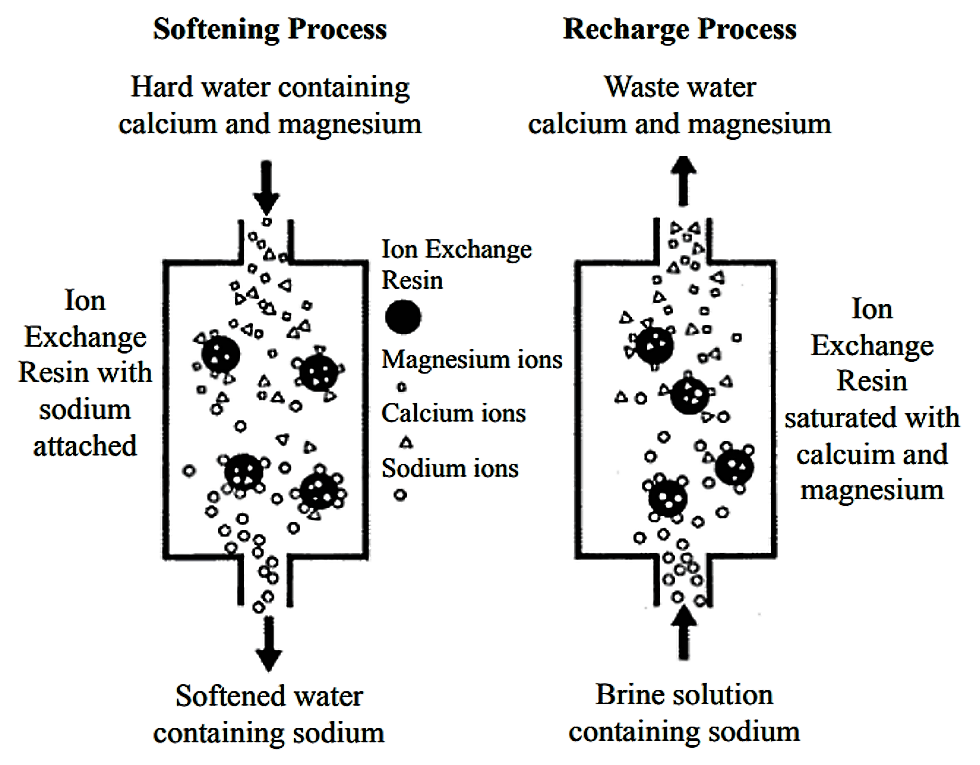
Softening Hard Water
Hard water contains calcium and magnesium ions. These ions cause scale buildup in pipes and appliances. Ion exchange resins replace calcium and magnesium with sodium ions. This process softens the water and prevents damage. Soft water also improves soap effectiveness and reduces stains.
Removing Contaminants
Ion exchange resins remove harmful contaminants like heavy metals. Lead, mercury, and arsenic can be trapped and replaced with harmless ions. This reduces the risk of health problems. The resins also help remove nitrates and other pollutants. Clean water means safer drinking and better health.
Deionization And Demineralization
Deionization removes all charged particles from water. Ion exchange resins exchange positive and negative ions for hydrogen and hydroxide ions. These ions combine to form pure water. Demineralization removes salts and minerals to create very pure water. This water is important for labs, industries, and medical use.
Credit: sswm.info
Advantages Of Using Ion Exchange Resins
Ion exchange resins offer many benefits that make them popular for water treatment and other applications. They help remove unwanted ions efficiently. These resins work quickly, saving time and energy. They also last long because they can be reused after regeneration. These advantages make ion exchange resins a smart choice for many industries.
Efficiency And Speed
Ion exchange resins remove ions from water fast and effectively. They have a large surface area that attracts ions quickly. This speeds up the purification process. The resins work continuously without losing performance. This means more water can be treated in less time. Their efficiency helps reduce energy and operational costs.
Regeneration And Reusability
One key benefit is that ion exchange resins can be regenerated. After use, they can be cleaned and restored to work again. This process allows multiple cycles of use. It lowers the need to replace the resin often. Regeneration saves money and reduces waste. It also supports sustainable and eco-friendly water treatment.
Challenges And Limitations
Ion exchange resins are useful in many processes but face some challenges. These challenges affect their performance and lifespan. Understanding these limits helps in better use and care of the resins.
Fouling And Resin Degradation
Fouling happens when particles block the resin surface. Dirt, oils, or organic matter cause fouling. This reduces the resin’s ability to exchange ions. Over time, fouling can stop the resin from working well.
Resin degradation is another issue. Harsh chemicals or high temperatures can break down the resin. This makes the resin weak and less effective. Regular cleaning and proper use can slow degradation.
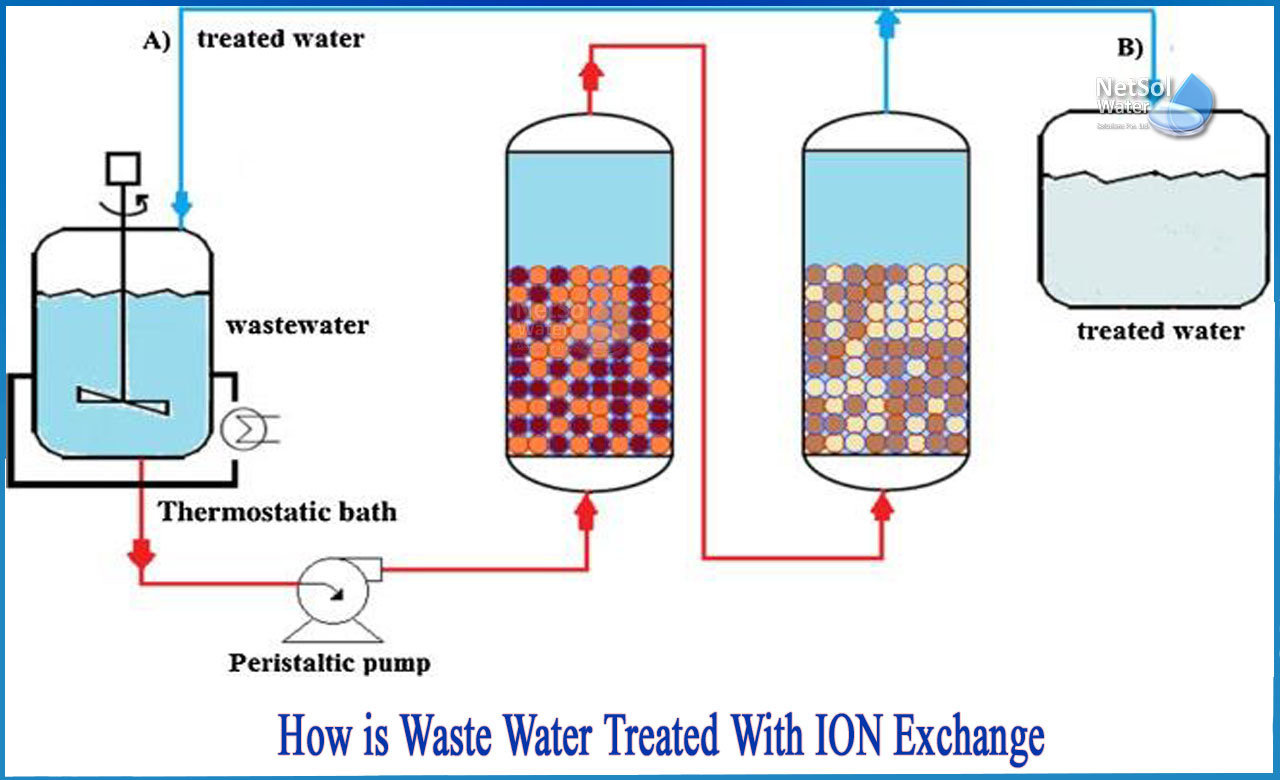
Handling And Disposal
Handling ion exchange resins requires care. Some resins can be harmful if touched or inhaled. Workers should use gloves and masks to stay safe.
Disposal of used resins is tricky. They may contain harmful ions and chemicals. Proper disposal methods prevent pollution and harm to the environment. Following local rules for disposal is important.
Credit: www.netsolwater.com
Future Trends In Ion Exchange Technology
The future of ion exchange technology holds many promising developments. These advances aim to improve efficiency and widen its applications. Scientists and engineers focus on making resins stronger and more selective. Combining ion exchange with other methods also shows great potential. These trends will help industries manage water and chemicals better.
Advanced Resin Materials
New materials improve ion exchange resins. These materials increase capacity and durability. They also resist fouling and chemical damage. Researchers explore polymers with special properties. These resins can target specific ions more precisely. This focus helps in water softening and waste treatment. Enhanced resins reduce costs by lasting longer. They also work faster, saving time and energy.
Integration With Other Purification Methods
Ion exchange technology pairs well with other purification techniques. Combining it with filtration or membrane processes improves results. This integration removes more contaminants from water. It also lowers the load on each method. Hybrid systems become more efficient and reliable. Industries benefit from cleaner water and less waste. This trend supports sustainable and cost-effective solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Ion Exchange Resins Used For?
Ion exchange resins are mainly used to soften water and remove contaminants. They exchange unwanted ions with beneficial ones. This process improves water quality for industrial and household use. They are also used in purification and separation applications.
How Do Ion Exchange Resins Remove Impurities?
Ion exchange resins remove impurities by swapping ions in water with resin ions. The resin attracts harmful ions like calcium or heavy metals. These ions attach to the resin, replacing harmless ions like sodium. This exchange cleans the water effectively.
What Types Of Ions Can Ion Exchange Resins Target?
Ion exchange resins can target cations like calcium, magnesium, and heavy metals. They also target anions such as chloride, nitrate, and sulfate. Different resins specialize in exchanging specific ion types to suit various purification needs.
How Often Should Ion Exchange Resins Be Regenerated?
Ion exchange resins need regeneration when their capacity declines. This typically occurs after processing a certain water volume or time. Regeneration uses salt or acid solutions to restore resin effectiveness. Regular regeneration ensures consistent water purification.
Conclusion
Ion exchange resins clean water by swapping unwanted ions. They work fast and can remove many harmful substances. These resins help make water safer for homes and industries. Knowing how they work shows why they matter so much. Choosing the right resin improves water quality easily.
Simple science with big effects. That’s the power of ion exchange resins.

Hasan Al Sarker is a Reverse Osmosis Specialist. He has worked for many years to ensure safe drinking water for all. His research paper has been published in several journals, including Issue, Medium, and Slideshare. He is recognized as a water doctor among specialists though he did not attend medical college.
Besides working as a researcher of reverse osmosis technology, he is also very fancy with the kitchen and cooking. His guides are reading thousands of people every day. As a head of content, he is responsible for all the published articles at RO System Reviews.

