Are you tired of dealing with hard water that leaves spots on your dishes and makes your soap less effective? You’re not alone.
Hard water can cause a lot of frustration in your daily routine. But what if there was a simple way to fix it? Understanding how ion exchange resin softens water can change the way you care for your home and your skin.
You’ll discover the secret behind this powerful method and why it’s the key to softer, cleaner water. Keep reading to find out how it works and how it can make a difference for you.
What Is Ion Exchange Resin
Ion exchange resin is a key material used to soften hard water. It helps remove minerals that make water hard. This resin plays an important role in water treatment systems. Understanding what ion exchange resin is can help explain how water softening works.
Composition And Types
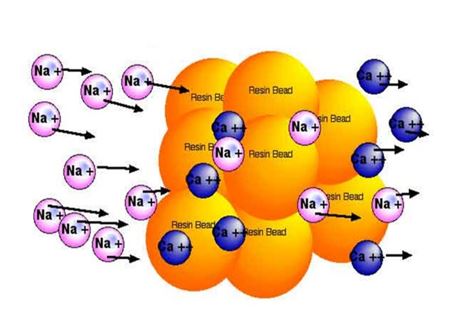
Ion exchange resin is made of small plastic beads. These beads are porous and have charged sites. The resin beads carry either positive or negative charges. The most common type used for softening water is cation exchange resin. It removes positively charged minerals like calcium and magnesium. Another type is anion exchange resin, which removes negatively charged ions. The resin’s structure holds ions tightly but can swap them with others.
How It Works Chemically
Ion exchange resin works by exchanging ions in water. Hard water contains calcium and magnesium ions. These ions cause water hardness. The resin beads hold sodium ions. When hard water passes through, the resin swaps sodium ions for calcium and magnesium. This swap removes hardness minerals from the water. The resin captures the hard ions and releases sodium. This chemical exchange process softens the water effectively.

Credit: www.lanlangcorp.com
Water Hardness Causes
Water hardness happens because of minerals dissolved in the water. These minerals come from rocks and soil. They mix with water as it moves through nature. Hard water causes many problems at home and in industries. Understanding what causes water hardness helps to find the right solution.
Common Minerals Involved
Calcium and magnesium are the main minerals causing hardness. These minerals dissolve in water naturally. Other minerals like iron and manganese also add to hardness sometimes. The amount of these minerals varies by location. High levels make water hard and affect its quality.
Effects On Plumbing And Appliances
Hard water creates scale buildup inside pipes and fixtures. This buildup blocks water flow and lowers pressure. It also damages water heaters and washing machines. Scale reduces appliance efficiency and increases energy use. Over time, plumbing repairs become more frequent and costly.
Softening Process Explained
Water softening removes minerals that make water hard. Hard water contains calcium and magnesium ions. These minerals cause scale and reduce soap effectiveness. Ion exchange resin is a common way to soften water. It swaps hard minerals with softer ones. This process improves water quality for daily use.
Ion Exchange Mechanism
The ion exchange resin holds sodium ions. It attracts calcium and magnesium ions from hard water. The resin captures these hard ions and releases sodium ions. This swap changes hard water into soft water. The resin works like a magnet for minerals. It traps hardness and frees the water from scaling effects.
Role Of Sodium And Calcium Ions
Sodium ions in the resin replace calcium ions in water. Calcium ions cause hardness and leave deposits. Sodium ions do not cause scale or soap scum. The exchange reduces calcium and magnesium levels. This process protects pipes and improves cleaning. Sodium ions keep water soft and gentle.
Types Of Ion Exchange Resins
Ion exchange resins play a key role in softening water. They come in different types, each designed for specific tasks. Understanding these types helps explain how water softening works effectively. Two main categories exist: cation exchange resins and anion exchange resins.
Cation Exchange Resins
Cation exchange resins remove positive ions from water. Common ions removed include calcium and magnesium. These ions cause water hardness. The resin swaps them with sodium or hydrogen ions. This exchange softens the water and prevents scale build-up. Cation resins are typically made from a plastic material with charged sites. These sites attract and hold onto the hard ions.
Anion Exchange Resins
Anion exchange resins target negative ions in water. They remove ions like chloride, nitrate, and sulfate. These ions can cause water to taste bad or corrode pipes. The resin replaces these ions with hydroxide ions. This process improves water quality and balance. Anion resins also consist of a plastic matrix with charged groups. These groups capture unwanted negative ions efficiently.
Advantages Of Using Ion Exchange Resins
Ion exchange resins offer clear benefits for softening water. They remove hardness-causing minerals effectively. These resins make water safer for daily use. They also improve water taste and reduce scale buildup in pipes. Many homes and industries trust ion exchange resins for water treatment.
Efficiency And Effectiveness
Ion exchange resins work quickly to soften water. They swap hard minerals like calcium and magnesium with sodium ions. This process lowers water hardness instantly. Resins handle large volumes of water without losing power. They keep working well over time with proper care. This makes them reliable for continuous water softening.
Cost And Maintenance Benefits
Using ion exchange resins can save money. They reduce damage to plumbing and appliances caused by hard water. Lower repair costs follow. These resins need minimal maintenance. Regular regeneration with salt restores their softening ability. The process is simple and inexpensive. This keeps overall costs low for users.
Credit: www.envirogengroup.com
Regeneration Of Resin Beads
Ion exchange resins soften water by removing hard minerals like calcium and magnesium. Over time, these resin beads lose their ability to soften water. This happens because they get full of the minerals they capture. The resin beads need a process called regeneration to work well again. Regeneration cleans the beads and prepares them for more softening.
Process And Chemicals Used
The regeneration process uses a strong salt solution. This solution contains sodium chloride, commonly known as salt. The salt solution flows through the resin tank. It pushes out the trapped calcium and magnesium ions. The resin beads then regain their sodium ions. This restores their ability to soften water. After this, the resin beads are ready to remove hardness again.
Frequency And Indicators
How often to regenerate depends on water hardness and usage. Higher hardness or more water use means more frequent regeneration. Some systems regenerate automatically after a set time or volume of water. Signs include a drop in water softness or a change in taste. Regular checks help keep the system working well. Proper regeneration ensures soft water all the time.
Applications Beyond Water Softening
Ion exchange resin is famous for softening water. It removes calcium and magnesium ions that cause hardness. But its use goes far beyond home water softening systems. This material plays a key role in many industries and helps protect the environment.
Its ability to swap ions makes it useful in many processes. It can capture harmful substances and recover valuable materials. The resin’s flexibility and efficiency make it a popular choice worldwide.
Industrial Uses
Industries use ion exchange resin to purify liquids and chemicals. It removes unwanted ions from water and process streams. This helps improve product quality and protect machines from damage.
In the food and beverage sector, it cleans sugar and sweeteners. It helps remove colors and impurities, making products clearer and tastier. In pharmaceuticals, the resin purifies raw materials and final products. This ensures safety and effectiveness.
Metal plating industries use resin to recover metals like gold and silver. This lowers waste and saves money. Power plants also use ion exchange resin to treat boiler water. It prevents scale and corrosion, extending equipment life.
Environmental Applications
Ion exchange resin helps reduce pollution by removing harmful ions from wastewater. It captures heavy metals, nitrates, and other toxins before water returns to nature. This protects rivers, lakes, and soil from damage.
The resin also supports recycling efforts. It recovers valuable elements from industrial waste, allowing reuse. This reduces the need for mining and lowers environmental impact.
In water treatment plants, it improves drinking water quality. It removes contaminants that harm health. Its role in clean water access is vital for communities worldwide.
Common Issues And Troubleshooting
Ion exchange resin softeners work well but can face issues over time. Troubleshooting common problems helps keep water soft and clean. Knowing signs of resin failure and maintenance tips improves resin life and performance.
Signs Of Resin Failure
Water may feel hard or have a strange taste. White spots can appear on dishes or glassware. Soap might not lather well during washing. The resin bed may show unusual odor or discoloration. Water flow might slow down or stop completely. These signs indicate resin needs attention or replacement.
Maintenance Tips
Regularly check salt levels in the brine tank. Clean the resin bed with special cleaners to remove iron and other minerals. Avoid using harsh chemicals that harm resin beads. Flush the system to remove trapped particles. Schedule professional inspection once a year. Proper care keeps the resin working efficiently for years.
Future Trends In Ion Exchange Technology
Ion exchange technology continues to evolve. New trends improve water softening efficiency and eco-friendliness.
These advancements aim to reduce costs and environmental impact. They promise better performance and longer resin life.
Innovations In Resin Materials
Researchers develop new resin materials with higher capacity. These resins capture more hardness ions in less time.
Improved resins resist fouling and chemical damage. This extends their use without frequent replacement.
Some new resins work well at lower regeneration levels. This saves water and salt during softening cycles.
Sustainability Focus
Modern ion exchange systems prioritize sustainability. They reduce chemical use and wastewater output.
Eco-friendly regeneration methods minimize salt discharge. This protects soil and nearby water sources.
Biodegradable resins and recyclable materials gain attention. This lowers waste and supports green water treatment.

Credit: www.ecowater-softeners.co.uk
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Ion Exchange Resin In Water Softening?
Ion exchange resin is a material that removes hardness ions like calcium. It exchanges them for sodium or potassium ions. This process softens hard water effectively, preventing scale buildup and improving water quality.
How Does Ion Exchange Resin Remove Hardness?
The resin attracts and holds calcium and magnesium ions. It swaps these hardness ions with sodium or potassium ions. This exchange softens the water without adding harmful chemicals.
Why Use Ion Exchange Resin For Water Softening?
Ion exchange resin is efficient and reusable. It provides consistent soft water and reduces scale damage. It also improves soap performance and extends appliance life.
How Often Should Ion Exchange Resin Be Replaced?
Resin lifespan depends on water hardness and usage. Typically, it lasts 5 to 10 years. Regular regeneration and maintenance can extend its effectiveness.
Conclusion
Ion exchange resin removes hard minerals from water effectively. It swaps calcium and magnesium ions with sodium ions. This process makes water soft and better for daily use. Soft water protects pipes and appliances from damage. It also helps soap work better and saves money on cleaning.
Using ion exchange resin is a simple way to improve water quality. It keeps your water gentle and safe for your home. Understanding this process helps you choose the right water softener. Soft water means less buildup and easier maintenance overall.

Hasan Al Sarker is a Reverse Osmosis Specialist. He has worked for many years to ensure safe drinking water for all. His research paper has been published in several journals, including Issue, Medium, and Slideshare. He is recognized as a water doctor among specialists though he did not attend medical college.
Besides working as a researcher of reverse osmosis technology, he is also very fancy with the kitchen and cooking. His guides are reading thousands of people every day. As a head of content, he is responsible for all the published articles at RO System Reviews.

