Have you ever wondered how your water gets so clean and fresh, especially when it tastes different from the tap? The secret often lies in a process called ion exchange water treatment.
This method can transform hard, mineral-filled water into soft, pure water that’s better for your skin, appliances, and even your health. If you want to know exactly how ion exchange works and why it might be the solution you need for better water, keep reading.
By the end, you’ll understand how this simple yet powerful process can make a big difference in your daily life.
Basics Of Ion Exchange
Understanding the basics of ion exchange helps explain how this water treatment works. It removes unwanted minerals and replaces them with safer ones. This process improves water quality for drinking and other uses.
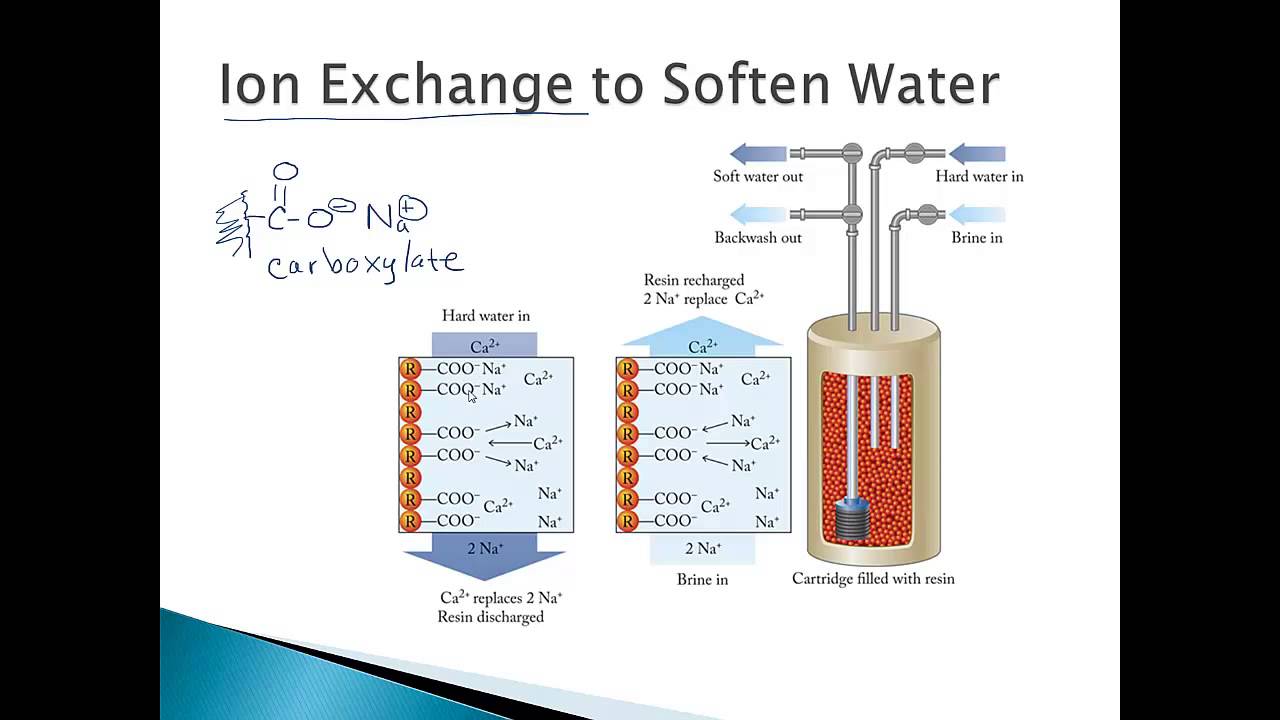
Ion exchange is a simple chemical process. It involves exchanging harmful ions in water with useful ions held by a resin. This exchange happens inside a tank filled with tiny beads called ion exchange resins.
What Is Ion Exchange
Ion exchange is a method that swaps ions between water and a solid material. The solid material is usually a resin with charged particles. It attracts and holds specific ions from the water. Then, it releases different ions back into the water.
This process removes unwanted ions like calcium, magnesium, or heavy metals. It replaces them with ions like sodium or hydrogen. This makes the water softer and safer for use.
Types Of Ion Exchange Resins
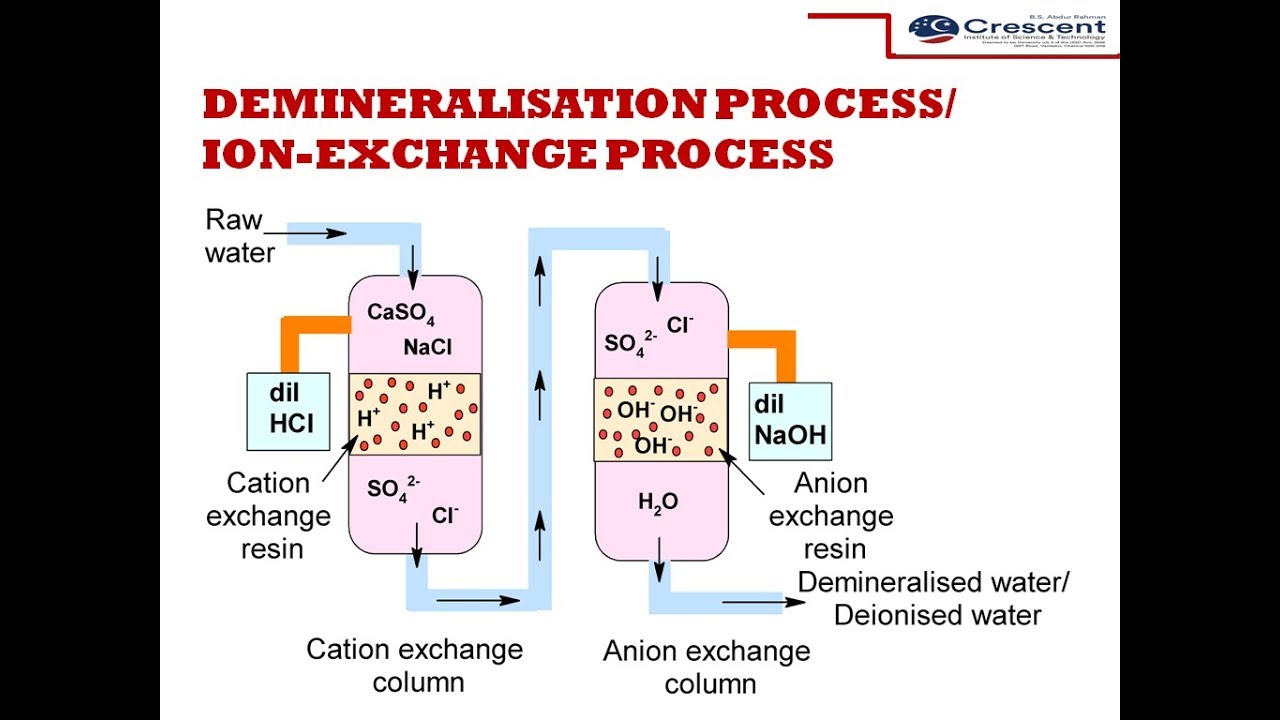
There are two main types of ion exchange resins: cation and anion resins. Cation resins exchange positively charged ions. They remove hardness ions like calcium and magnesium.
Anion resins exchange negatively charged ions. They help remove contaminants like nitrate, sulfate, and chloride. Each resin type targets specific ions based on their charge.
Resins come in different forms and strengths. The choice depends on the water treatment needs. Some resins work better for softening, others for removing toxic ions.
Process Of Ion Exchange
The process of ion exchange is a common method for treating water. It removes unwanted ions and replaces them with useful ones. This process makes water safer and better for use. Understanding how ion exchange works helps to appreciate its benefits.
Ion Exchange Mechanism
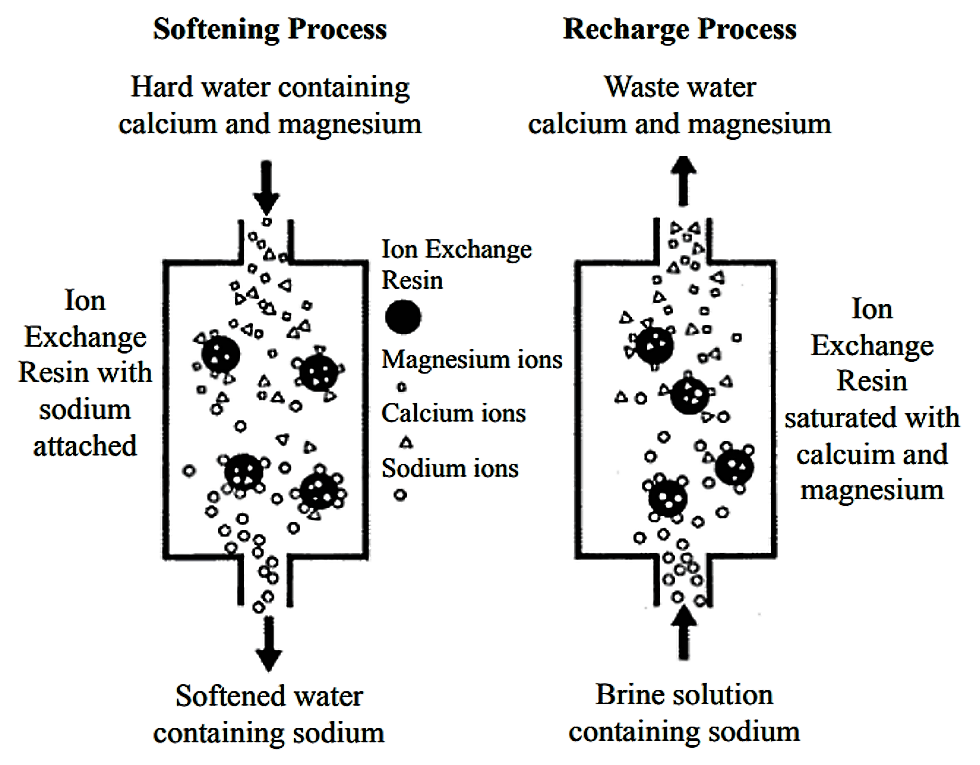
Ion exchange works by swapping ions in water with ions on a solid material. This solid material is called a resin. The resin holds charged particles, called ions. When water passes through the resin, unwanted ions stick to it. At the same time, the resin releases different ions into the water. This swap cleans the water by removing harmful substances.
Stages Of Treatment
The treatment has several stages. First, water enters the ion exchange tank. Here, ions like calcium and magnesium attach to the resin. These ions cause hardness in water. Next, the resin releases sodium or hydrogen ions. This exchange softens the water and removes impurities. Finally, clean water leaves the tank, ready for use.
Regeneration Cycle
Over time, the resin fills up with unwanted ions. It loses its ability to clean water. To fix this, the resin goes through regeneration. A special solution flushes the resin. This solution removes the trapped ions. The resin then regains its cleaning power. The cycle repeats to keep water treatment effective.
Applications Of Ion Exchange
Ion exchange is a key process used in many water treatment applications. It helps remove unwanted minerals and impurities from water. This process improves water quality for various uses. Below are some common applications of ion exchange in water treatment.
Water Softening
Water softening is one of the most common uses of ion exchange. Hard water contains calcium and magnesium ions that cause scale buildup. Ion exchange replaces these ions with sodium or potassium ions. This prevents scale and makes water gentler on pipes and appliances.
Deionization And Demineralization
Deionization removes almost all mineral ions from water. It uses ion exchange resins to replace charged particles with hydrogen and hydroxide ions. This process produces very pure water. Demineralization is crucial in labs and industries needing clean water for processes.
Industrial Uses
Industries rely on ion exchange for many tasks. It treats boiler water to stop corrosion and scaling. It also helps in food processing and pharmaceutical manufacturing. Ion exchange cleans water for cooling systems and removes pollutants from wastewater.
Credit: www.youtube.com
Advantages And Limitations
Ion exchange water treatment offers many benefits but also has some limits. Understanding both helps in deciding if it suits your water needs. This section explains the main advantages and common challenges of this method.
Benefits Of Ion Exchange
Ion exchange removes hard minerals like calcium and magnesium. This improves water softness and taste. It also helps protect pipes and appliances from scale buildup. The process works quickly and efficiently. It can treat large volumes of water. The system is easy to operate and maintain. It does not use harmful chemicals, making it safe for homes. It also reduces contaminants like heavy metals and nitrates.
Common Challenges
Ion exchange needs regular maintenance to work well. The resin inside the system wears out over time. It requires salt or other regenerants to recharge. This adds to the ongoing cost. It may not remove all types of contaminants. Water with high iron or organic matter can clog the resin. Waste brine from regeneration must be disposed of properly. This can affect the environment if not handled well.
Maintaining Ion Exchange Systems
Maintaining ion exchange systems ensures they work well and last longer. Proper care keeps the water clean and the system efficient. Routine checks and small fixes prevent major problems.
Monitoring Performance
Check water quality regularly to see if the system works. Measure hardness or contaminants before and after treatment. Track flow rates and pressure to find issues early. Keep a log of all readings for comparison.
Troubleshooting Issues
Look for changes in water taste or smell as warning signs. Inspect resin beads for damage or clogging. Check for leaks or unusual noises in the system. Follow the manual to fix common problems quickly.
Best Practices For Longevity
Clean the system parts regularly to avoid buildup. Use the correct salt type for resin regeneration. Replace worn-out parts on time to prevent damage. Avoid harsh chemicals that can harm the resin. Schedule professional service annually to ensure top performance.
Credit: sswm.info
Credit: www.youtube.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Ion Exchange In Water Treatment?
Ion exchange is a process that removes unwanted ions from water. It replaces harmful ions with beneficial ones using resin beads. This improves water quality by softening or demineralizing it, making it safer for consumption and industrial use.
How Does Ion Exchange Resin Work?
Ion exchange resin contains charged beads that attract and hold specific ions. When water passes through, harmful ions swap places with harmless ones on the resin. This continuous exchange cleans water efficiently without adding chemicals.
What Contaminants Can Ion Exchange Remove?
Ion exchange effectively removes hardness ions like calcium and magnesium. It also eliminates heavy metals, nitrates, and certain radioactive elements. This process is ideal for softening water and reducing toxic contaminants.
How Often Should Ion Exchange Resin Be Replaced?
Resin lifespan depends on water quality and usage. Typically, resin lasts 3 to 5 years before needing replacement. Regular regeneration extends resin life by flushing out trapped ions and restoring its effectiveness.
Conclusion
Ion exchange water treatment cleans water by swapping harmful ions. It removes minerals like calcium and magnesium that cause hardness. This process helps protect pipes and improves water taste. The system uses resin beads that trap unwanted ions. Water flows through the beads, leaving cleaner water behind.
Regular maintenance keeps the system working well. Many homes and industries use ion exchange for better water quality. Understanding this method shows how simple science improves daily life. Clean water matters. Ion exchange makes it possible.

Hasan Al Sarker is a Reverse Osmosis Specialist. He has worked for many years to ensure safe drinking water for all. His research paper has been published in several journals, including Issue, Medium, and Slideshare. He is recognized as a water doctor among specialists though he did not attend medical college.
Besides working as a researcher of reverse osmosis technology, he is also very fancy with the kitchen and cooking. His guides are reading thousands of people every day. As a head of content, he is responsible for all the published articles at RO System Reviews.

