Have you ever wondered how water gets rid of unwanted minerals and becomes safe to drink? The secret often lies in a process called ion exchange.
This simple yet powerful method can transform hard, mineral-filled water into clean, fresh water for your home or business. Understanding how ion exchange works can help you make better choices for your water treatment needs. Keep reading to discover how this technique removes impurities and why it might be the perfect solution for your water problems.
Basics Of Ion Exchange
Ion exchange is a common method to clean and soften water. It works by swapping unwanted ions in water with safer ones. This process helps remove hard minerals and other impurities. Understanding the basics of ion exchange can clarify how water treatment systems work efficiently.
The process involves special materials called resins. These resins attract certain ions and release others. This exchange changes the water’s chemical makeup, making it cleaner and safer for use. Below, we explore key parts of ion exchange in water treatment.
What Is Ion Exchange
Ion exchange is a chemical process. It swaps one type of ion in water for another. The process uses solid materials called ion exchange resins. These resins hold charged particles that attract opposite charges. When water passes through, the resin grabs unwanted ions and releases harmless ones.
This process removes minerals like calcium and magnesium. It also reduces contaminants such as heavy metals. Ion exchange can soften water or purify it depending on the resin used.
Types Of Ion Exchange Resins
There are two main types of ion exchange resins: cation and anion resins. Cation resins attract positively charged ions. These include calcium, magnesium, and iron. Anion resins attract negatively charged ions like chloride, nitrate, and sulfate.
Some water treatment systems use both types for complete purification. The choice depends on the water quality and treatment goals.
Common Ions In Water
Water contains many ions naturally. Calcium and magnesium cause water hardness. Sodium and potassium are also common. Chloride and sulfate can affect taste and corrosion. Heavy metals like lead and iron may be present in polluted water.
Ion exchange targets these ions to improve water quality. Removing hard minerals protects pipes and appliances. Reducing harmful ions makes water safer to drink.
Ion Exchange Process
The ion exchange process is a key method in water treatment. It helps remove unwanted minerals and impurities from water. This process works by swapping harmful ions with safer ones. It improves water quality for drinking, cooking, and industrial use.
How Ions Are Swapped
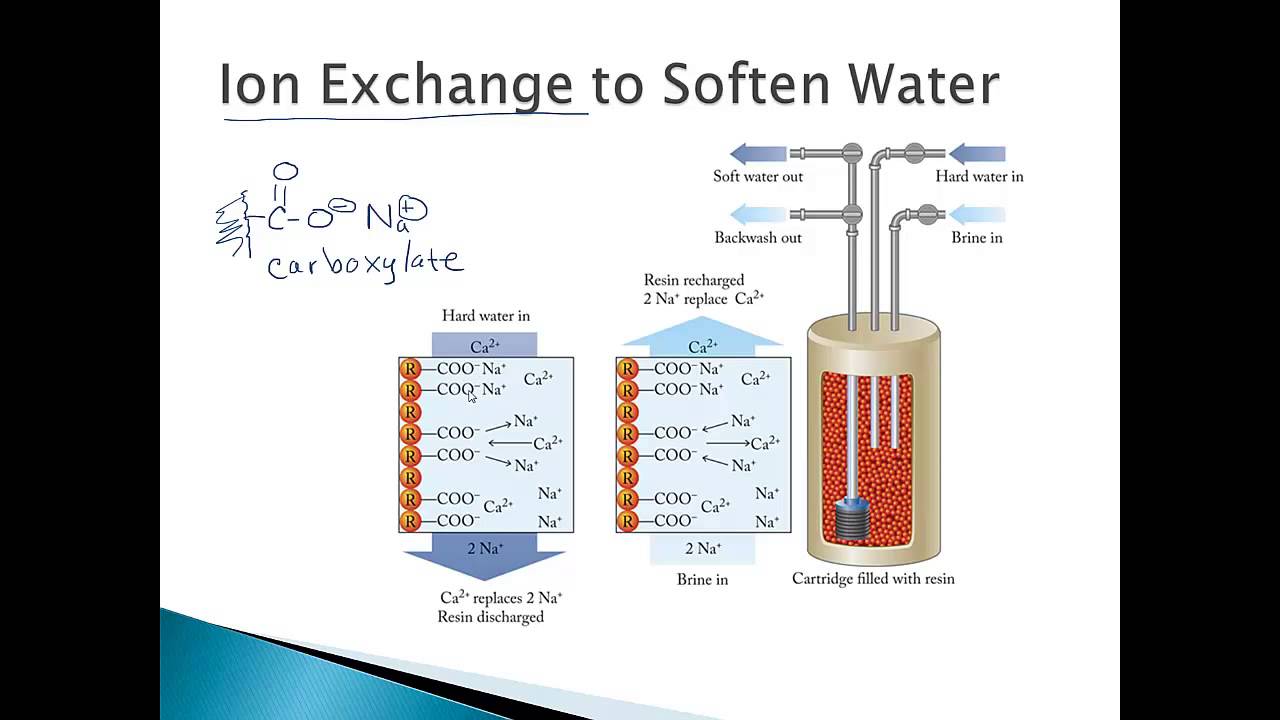
In ion exchange, ions in water are replaced by ions on a solid material. The solid holds ions that are easy to swap. Harmful ions in water attach to the solid, and safer ions take their place in the water. This swap cleans the water by removing bad ions like calcium or lead.
Role Of Resin Beads
Resin beads are tiny, plastic balls that hold ions tightly. These beads have charged sites that attract specific ions. They act like magnets for unwanted ions in water. The beads release safe ions while capturing the bad ones. Resin beads are the heart of the ion exchange system.
Flow Of Water Through Resin
Water flows through a tank filled with resin beads. As water moves, ions swap between the water and beads. The resin catches harmful ions from the water. Clean water leaves the tank with fewer impurities. This flow ensures continuous removal of unwanted minerals.
Applications In Water Treatment
Ion exchange plays a key role in water treatment. It improves water quality by changing unwanted ions into safer ones. This process suits many water treatment needs. Its flexibility makes it useful in homes, industries, and water plants.
Softening Hard Water
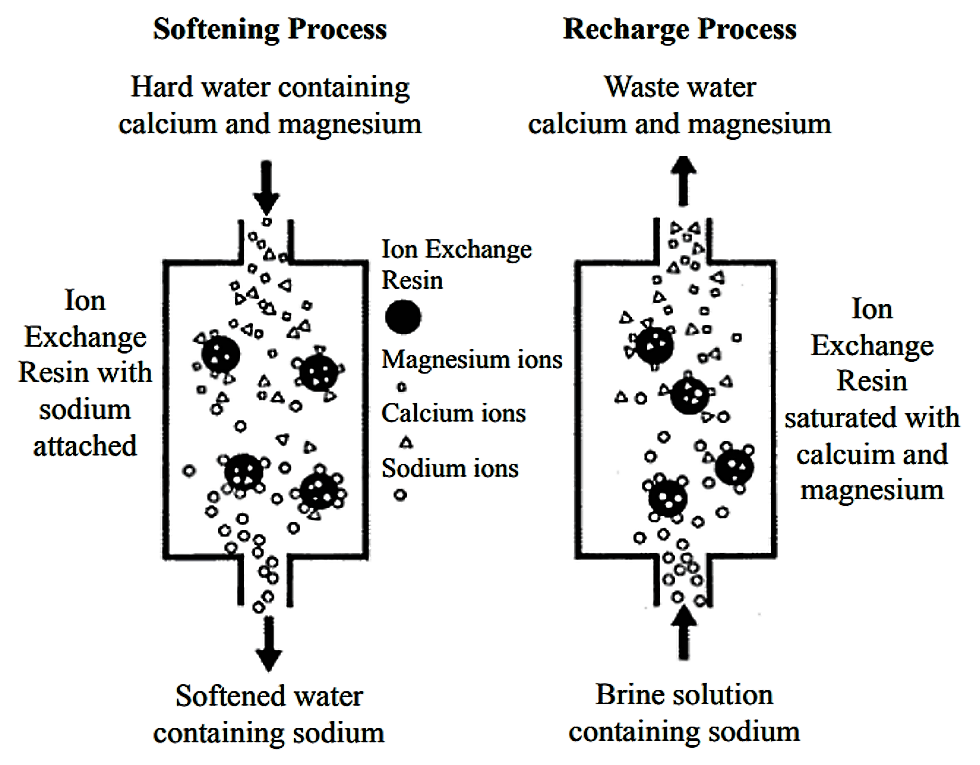
Hard water contains minerals like calcium and magnesium. These minerals cause scale buildup in pipes and appliances. Ion exchange replaces these minerals with sodium or potassium ions. This change prevents scale and makes water gentler on skin and clothes. Many households use ion exchange systems to soften their water daily.
Removing Contaminants
Ion exchange removes harmful contaminants from water. It captures heavy metals such as lead, mercury, and arsenic. These metals are replaced with less harmful ions. This helps protect human health and the environment. Water treatment plants use ion exchange to meet safety standards. It also removes nitrates and other pollutants efficiently.
Deionization And Demineralization
Deionization removes all charged particles from water. This produces very pure water for labs and industries. Demineralization is similar but targets mineral salts specifically. Ion exchange resins trap these ions and release hydrogen or hydroxide ions. The result is water free from dissolved solids. This pure water is essential in electronics, pharmaceuticals, and power plants.
Credit: sswm.info
Types Of Ion Exchange Systems
Ion exchange systems play a key role in water treatment. They remove unwanted ions and replace them with safer ones. Different types of ion exchange systems serve different purposes. Each type targets specific contaminants in water. Understanding these types helps in choosing the right system for clean water.
Cation Exchange Systems
Cation exchange systems remove positively charged ions from water. Common ions removed include calcium, magnesium, and iron. These ions cause hardness and scaling in pipes. The system replaces harmful cations with sodium or hydrogen ions. This process softens the water and prevents buildup. Cation exchange is widely used in water softeners.
Anion Exchange Systems
Anion exchange systems target negatively charged ions. These ions include nitrate, sulfate, and chloride. The system swaps these ions with hydroxide or chloride ions. It helps reduce water acidity and remove harmful contaminants. Anion exchange improves water taste and safety. It is often used in drinking water treatment.
Mixed Bed Systems
Mixed bed systems combine both cation and anion exchange resins. This setup removes both positive and negative ions simultaneously. It produces very pure water by reducing total dissolved solids. Mixed bed systems are common in laboratories and industrial applications. They provide the highest level of water purification.
Maintenance And Regeneration
Maintenance and regeneration are key to keeping ion exchange systems efficient. Over time, the resin inside the system loses its ability to remove unwanted ions. Regular checks and proper care extend the life of the resin. This section explains how to spot resin exhaustion, the steps in regeneration, and safe handling of materials.
Signs Of Resin Exhaustion
Resin exhaustion means the resin cannot clean water well anymore. Look for changes in water taste or odor. A rise in water hardness or unwanted chemicals shows resin wear. Low water flow or strange colors in water also signal resin problems. Timely detection helps avoid poor water quality.
Regeneration Process
Regeneration restores the resin’s ability to remove ions. It involves flushing the resin with a special chemical solution. Commonly, salt brine is used for this purpose. The solution replaces the trapped ions with sodium or hydrogen ions. This process takes a few hours and returns the resin to full strength.
Handling And Disposal
Handle regeneration chemicals carefully to avoid hazards. Wear gloves and eye protection during the process. Dispose of spent brine and waste water according to local rules. Do not pour chemicals directly into drains or soil. Proper disposal protects the environment and complies with regulations.
Advantages And Limitations
Ion exchange is a popular method in water treatment. It removes unwanted ions and replaces them with useful ones. This process improves water quality but has both advantages and limitations. Understanding these helps to choose the right water treatment system.
Benefits Of Ion Exchange
Ion exchange removes hardness, heavy metals, and nitrates effectively. It improves taste, smell, and clarity of water. The process works quickly and continuously. It can treat large volumes of water at once. Ion exchange resins are reusable after regeneration. This makes the method eco-friendly and efficient.
Common Challenges
Ion exchange may not remove all contaminants. Some organic compounds pass through untreated. The resins require regular regeneration using chemicals. Improper handling can cause resin damage. Ion exchange systems need skilled maintenance and monitoring. Fouling and scaling can reduce system performance.
Cost Considerations
Initial setup costs can be high. Resins and equipment must be replaced over time. Chemical costs for regeneration add to expenses. Operating costs depend on water quality and volume treated. Despite costs, ion exchange offers good value for clean water. It suits both homes and industries seeking reliable treatment.
Future Trends In Ion Exchange
The future of ion exchange in water treatment looks promising. New technologies and methods aim to improve efficiency and reduce costs. Innovations focus on making the process cleaner and more sustainable. These trends will shape how water treatment plants operate in the coming years.
Advancements In Resin Technology
Resins play a key role in ion exchange. Scientists are developing resins with higher capacity and selectivity. These new resins can remove more contaminants faster. Some resins work better at different temperatures and pH levels. This means they can handle tougher water conditions. Longer-lasting resins reduce the need for frequent replacements. This saves money and reduces waste.
Integration With Other Treatments
Ion exchange often works alongside other water treatments. Combining it with methods like filtration and reverse osmosis improves results. Hybrid systems remove more types of contaminants. This leads to safer and cleaner water. Integration also helps plants run more smoothly. Operators can choose the best mix of treatments for their water needs.
Sustainable Practices
Water treatment must be eco-friendly. New trends focus on reducing chemical use in ion exchange. Regeneration processes are becoming more efficient and less polluting. Some plants recycle the chemicals used in regeneration. Energy use is also being lowered with better equipment. Sustainable practices help protect the environment and save resources.
Credit: www.youtube.com

Credit: samcotech.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Ion Exchange In Water Treatment?
Ion exchange is a water purification process that removes unwanted ions. It swaps harmful ions with harmless ones using resin beads. This method effectively softens water and eliminates contaminants like heavy metals and hardness-causing minerals.
How Does Ion Exchange Resin Work?
Ion exchange resin contains charged beads that attract and hold specific ions. When water passes through, harmful ions bind to the resin. Simultaneously, beneficial ions like sodium or potassium are released, purifying the water efficiently.
What Contaminants Can Ion Exchange Remove?
Ion exchange removes hardness minerals like calcium and magnesium. It also eliminates heavy metals such as lead, copper, and iron. Additionally, it can reduce nitrate and arsenic levels, improving overall water quality.
Is Ion Exchange Safe For Drinking Water?
Yes, ion exchange is safe and widely used in drinking water treatment. It removes harmful ions without adding toxic chemicals. Properly maintained systems ensure clean, safe, and great-tasting water for consumption.
Conclusion
Ion exchange removes unwanted minerals from water effectively. It swaps harmful ions with safer ones. This process improves water taste and quality. Many homes and industries use ion exchange daily. It also helps protect plumbing and appliances. Understanding how it works can guide better water care.
Clean water supports health and comfort at home. Simple, reliable, and efficient—ion exchange serves many needs well.

Hasan Al Sarker is a Reverse Osmosis Specialist. He has worked for many years to ensure safe drinking water for all. His research paper has been published in several journals, including Issue, Medium, and Slideshare. He is recognized as a water doctor among specialists though he did not attend medical college.
Besides working as a researcher of reverse osmosis technology, he is also very fancy with the kitchen and cooking. His guides are reading thousands of people every day. As a head of content, he is responsible for all the published articles at RO System Reviews.

