Have you ever wondered how water is purified or how certain chemicals are separated so efficiently? The secret often lies in a powerful tool called ion exchange resins.
These tiny, bead-like materials work quietly behind the scenes to remove unwanted ions and replace them with others, making your water safer and your processes cleaner. If you want to understand how this technology can impact your daily life or industry, keep reading—because knowing what ion exchange resins are could change how you think about water treatment and chemical processing forever.
Credit: www.netsolwater.com
Basics Of Ion Exchange Resins
Ion exchange resins are small beads used in water treatment and chemical processes. They help remove unwanted ions from liquids. This makes water cleaner and safer for many uses.
The process works by swapping ions in the liquid with ions held by the resin. This exchange improves water quality and helps in many industries. Understanding the basics is key to knowing how they work.
Composition And Structure
Ion exchange resins are made of a polymer matrix. This matrix forms tiny beads, usually less than a millimeter wide. The beads have charged groups attached to them.
These charged groups attract and hold ions from the liquid. The structure allows liquids to pass through easily. The resin beads can be strong and last a long time.
Types Of Ion Exchange Resins
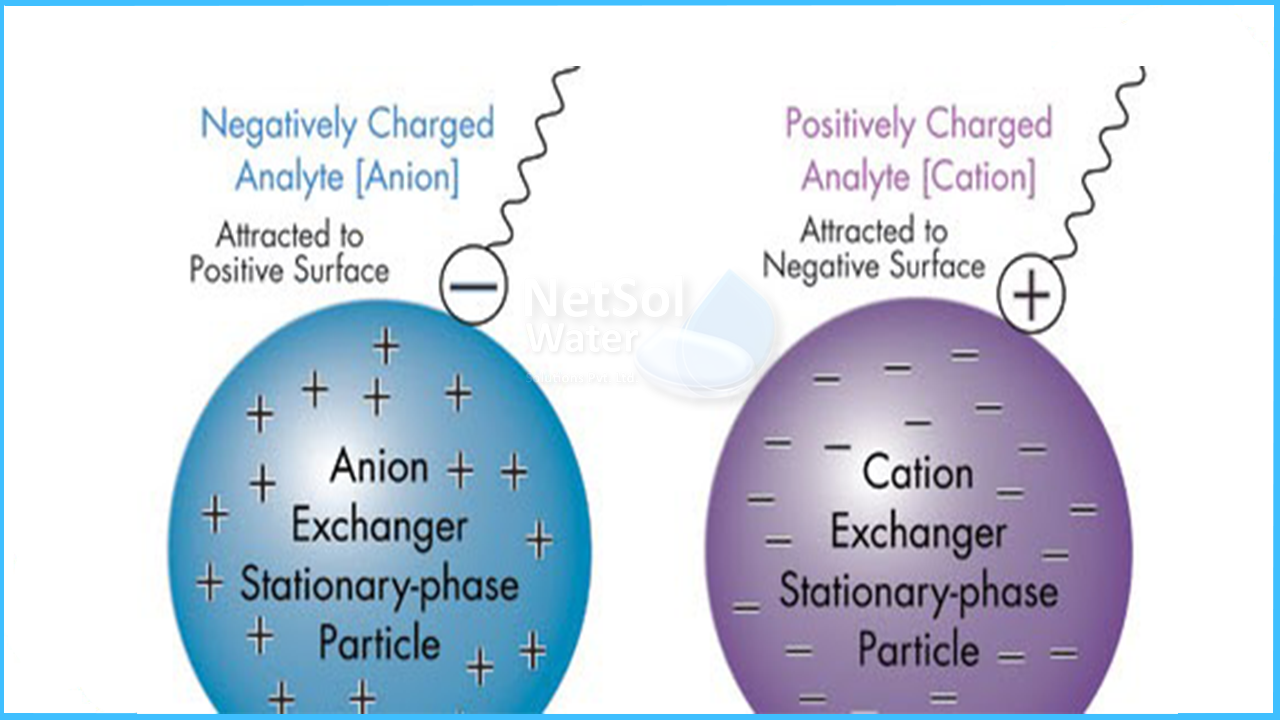
There are two main types of ion exchange resins: cation and anion resins. Cation resins swap positive ions like calcium and magnesium. Anion resins exchange negative ions like chloride and sulfate.
Some resins are strong acid or base types, while others are weak. Each type works best for different water conditions. Choosing the right resin depends on the problem to solve.

Credit: eaiwater.com
How Ion Exchange Resins Work
Ion exchange resins are small beads that clean water by swapping ions. These resins hold charged particles and exchange them with unwanted ions in water. This process helps remove impurities and soften hard water. Understanding how ion exchange resins work reveals their important role in water treatment and purification.
Ion Exchange Process
The ion exchange process starts with resin beads filled with specific ions. When water passes through, unwanted ions swap places with these ions on the beads. For example, calcium and magnesium ions in hard water are replaced by sodium ions from the resin. This exchange happens because the resin prefers certain ions and holds them tightly.
After some time, the resin loses its ions and becomes less effective. At this point, it undergoes regeneration. A strong solution flushes the resin, restoring its original ions. The resin is ready to clean water again. This cycle repeats many times in water treatment systems.
Factors Affecting Performance
The resin’s performance depends on several key factors. Water temperature affects how fast ions move and exchange. Higher temperatures speed up the process but can damage the resin.
The concentration of ions in the water also matters. Too many impurities can overload the resin quickly. Flow rate is important as well; water passing too fast reduces contact time and lowers efficiency.
Lastly, the resin’s age and type influence its capacity. Older resins lose strength and exchange ability. Choosing the right resin type matches specific water treatment needs.
Common Applications
Ion exchange resins serve many important roles in industries worldwide. These tiny beads help remove unwanted ions from liquids. Their ability to swap ions makes them useful in many processes. The following are some common uses of ion exchange resins.
Each application benefits from the resin’s unique chemistry. They improve water quality, protect machines, and ensure safety in food and medicine.
Water Softening
Ion exchange resins remove calcium and magnesium from hard water. This process stops scale buildup in pipes and appliances. Soft water extends the life of boilers and heaters. It also improves soap’s cleaning power. Many homes and industries use these resins to soften water easily.
Wastewater Treatment
These resins help clean industrial wastewater by removing harmful metals. They capture toxic ions like lead and mercury. This prevents pollution and protects the environment. Wastewater treatment plants use ion exchange to meet safety standards. The process makes water safe for reuse or release.
Food And Beverage Industry
Ion exchange resins purify liquids in food production. They remove unwanted minerals and colors from sugar and juice. Resins also help in water purification for beverages. This improves taste and quality. The food industry relies on these resins to maintain product safety and consistency.
Pharmaceutical Uses
Pharmaceutical companies use ion exchange resins to purify drugs and ingredients. They remove impurities and control pH levels in solutions. Resins also aid in drug delivery by releasing medicine slowly. These uses ensure medicines are safe and effective for patients.

Credit: www.ionicsystems.com
Benefits Of Using Ion Exchange Resins
Ion exchange resins offer many benefits in water treatment and other industries. They improve processes by removing unwanted ions effectively. These resins are easy to use and adaptable to various needs. Their advantages make them popular for both small and large-scale applications.
Efficiency And Selectivity
Ion exchange resins work fast and target specific ions. They remove hardness, heavy metals, and unwanted salts with high precision. This selectivity helps in producing pure water and chemicals. The process uses less energy than other methods. It also reduces waste by focusing only on harmful ions.
Environmental Advantages
Using ion exchange resins reduces chemical use and waste. They allow water to be reused, lowering overall consumption. These resins help avoid harmful discharges into rivers and soil. Their ability to regenerate means less solid waste is produced. This makes them a greener option for water treatment.
Cost-effectiveness
Ion exchange resins save money over time. They need less energy and fewer chemicals than other treatments. Their long life reduces the need for frequent replacement. The process also lowers maintenance costs. This makes ion exchange resins a budget-friendly solution for many industries.
Maintenance And Regeneration
Maintenance and regeneration keep ion exchange resins effective. These steps restore resin capacity and remove trapped impurities. Regular care improves water quality and extends resin life. Understanding cleaning and care methods helps optimize resin performance.
Cleaning Methods
Cleaning ion exchange resins removes dirt and organic matter. Rinsing with clean water flushes out loose particles. Using mild chemicals helps dissolve stubborn deposits. Acid cleaning removes scale and metal buildup. Base cleaning targets organic fouling and oils. Follow manufacturer guidelines for safe cleaning.
Extending Resin Life
Proper handling prevents resin damage and wear. Avoid exposure to chlorine or harsh chemicals. Monitor water quality to reduce contaminants. Regenerate resins regularly using correct salt or acid solutions. Store resins in moist conditions to prevent drying. Timely maintenance cuts replacement costs and downtime.
Future Trends And Innovations
The future of ion exchange resins holds many exciting possibilities. New technologies and materials aim to improve their efficiency and durability. These advancements help meet growing demands in water treatment, pharmaceuticals, and other industries.
Researchers focus on creating better resins that work faster and last longer. They also explore ways to make the resins more eco-friendly. These innovations will shape how ion exchange resins are used in the coming years.
Advanced Resin Materials
Scientists develop new resin materials with stronger structures. These materials resist damage from heat and chemicals. They improve the resin’s ability to capture unwanted ions. Faster exchange rates reduce treatment times and costs. Some resins are designed for specific uses, like removing heavy metals. This specialization increases their effectiveness in targeted applications.
Sustainability Improvements
Efforts to reduce environmental impact guide resin development. Biodegradable and recyclable resins are becoming more common. Lower energy processes help regenerate resins with less waste. Using natural raw materials reduces reliance on petroleum products. These steps make ion exchange technology greener and safer for the planet. Sustainability is key to future resin innovation.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Are Ion Exchange Resins Used For?
Ion exchange resins remove unwanted ions from liquids. They purify water, soften hard water, and separate ions in chemical processes. These resins are key in water treatment, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and food processing industries.
How Do Ion Exchange Resins Work?
Ion exchange resins swap ions in liquids with ions attached to their surface. This process cleans or softens the liquid by removing contaminants. The resin’s charged sites attract and hold specific ions, exchanging them for less harmful ones.
What Types Of Ion Exchange Resins Exist?
There are two main types: cation and anion exchange resins. Cation resins exchange positively charged ions, while anion resins exchange negatively charged ions. Both types serve different purification and separation purposes in various industries.
Why Are Ion Exchange Resins Important In Water Treatment?
They effectively remove hardness, heavy metals, and contaminants from water. This improves water quality and safety for drinking and industrial use. Ion exchange resins also regenerate easily, making them cost-effective for ongoing water treatment.
Conclusion
Ion exchange resins play a key role in water treatment and purification. They help remove unwanted minerals and ions from liquids. These resins work by swapping ions, making water cleaner and safer. Their use spans many industries, from drinking water to chemical processing.
Understanding their function helps appreciate their value in daily life. Simple, effective, and reliable—ion exchange resins continue to support many important processes.

Hasan Al Sarker is a Reverse Osmosis Specialist. He has worked for many years to ensure safe drinking water for all. His research paper has been published in several journals, including Issue, Medium, and Slideshare. He is recognized as a water doctor among specialists though he did not attend medical college.
Besides working as a researcher of reverse osmosis technology, he is also very fancy with the kitchen and cooking. His guides are reading thousands of people every day. As a head of content, he is responsible for all the published articles at RO System Reviews.

