Have you ever wondered what’s really in your tap water? You might be surprised to learn that water can carry minerals and impurities that affect its taste, safety, and how it interacts with your appliances.
That’s where ion exchange comes in—a powerful process that can transform your water by removing unwanted elements. If you want cleaner, better-tasting water for your home or business, understanding what ion exchange removes is key. Keep reading to discover how this method works and why it might be exactly what your water needs.
Basics Of Ion Exchange
Ion exchange is a common method to clean water. It removes unwanted minerals and particles. This process helps make water safer and better for use.
The technique uses special materials called resins. These resins swap harmful ions in water with safer ones. This swap changes the water’s quality quickly and efficiently.
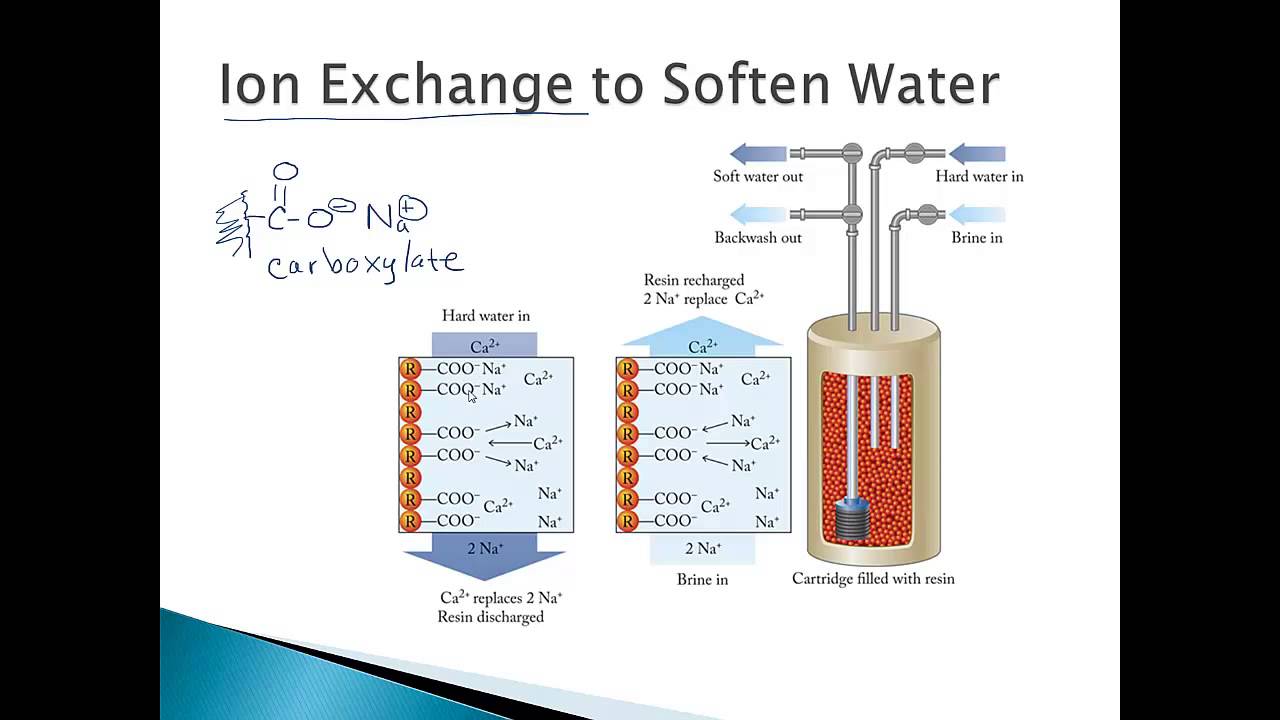
How Ion Exchange Works
Ion exchange works by swapping ions between water and resin. The resin holds ions with a positive or negative charge. When water passes through, the resin attracts unwanted ions.
These unwanted ions leave the water and attach to the resin. At the same time, the resin releases safe ions into the water. This exchange improves water by removing hardness, metals, and other contaminants.
Types Of Ion Exchange Resins
Two main types of resins exist: cation and anion resins. Cation resins remove positive ions like calcium and magnesium. These ions cause water hardness.
Anion resins remove negative ions such as nitrate and sulfate. These ions can cause bad tastes and odors. Choosing the right resin depends on the type of contaminant in the water.
Credit: www.youtube.com
Common Contaminants Removed
Ion exchange is a popular water treatment method. It removes many common contaminants. This process helps improve water quality for daily use. Understanding which contaminants ion exchange targets is important for choosing the right system.
Hardness Minerals
Hardness minerals like calcium and magnesium cause water hardness. Hard water can damage pipes and appliances. Ion exchange swaps these minerals with sodium or potassium ions. This softens the water and protects plumbing.
Heavy Metals
Heavy metals include lead, copper, and mercury. These metals pose health risks even in small amounts. Ion exchange removes them by exchanging harmful metal ions with safer ones. This makes drinking water safer and cleaner.
Nitrates And Nitrites
Nitrates and nitrites often come from fertilizers and waste. High levels in water can harm babies and adults. Ion exchange systems effectively reduce these contaminants. This helps protect your family from potential health issues.
Ammonium Ions
Ammonium ions come from fertilizers and sewage. They affect water taste and quality. Ion exchange replaces ammonium ions with harmless ions. This improves water quality for cooking and drinking.
Impact On Water Quality
Ion exchange changes water by removing unwanted minerals and chemicals. This process improves the quality of water in many ways. It helps make water cleaner, safer, and more pleasant to use every day.
Taste And Odor Improvements
Ion exchange removes metals like iron and manganese that cause bad taste and smell. It also reduces chlorine and other chemicals that give water a harsh odor. After treatment, water tastes fresher and smells cleaner. This makes drinking and cooking with water much better.
Reduction Of Scale Formation
Hard water minerals cause scale buildup in pipes and appliances. Ion exchange removes calcium and magnesium, the main culprits of scale. This helps protect water heaters, kettles, and plumbing systems. Less scale means appliances last longer and work more efficiently.
Credit: www.researchgate.net
Limitations Of Ion Exchange
Ion exchange is a common method to soften water and remove some contaminants. It works well for certain minerals but has limits. Understanding these limits helps in choosing the right water treatment.
Contaminants Not Removed
Ion exchange does not remove all contaminants. It cannot take out bacteria or viruses. Chemicals like pesticides and solvents also stay in the water. It mainly targets minerals like calcium and magnesium. Other harmful substances need different filters or treatments.
Resin Lifespan And Maintenance
The resin in ion exchange systems wears out over time. It needs regular cleaning and recharging with salt. Without maintenance, the resin loses effectiveness. Replacing the resin can be costly. Proper care ensures the system works well for longer.
Applications In Water Treatment
Ion exchange is a common method used to clean and soften water. It removes unwanted minerals and impurities. This process is useful in many water treatment settings. It helps improve water quality for different needs. Below are some key areas where ion exchange plays a vital role.
Residential Use
Many homes use ion exchange to soften hard water. Hard water has minerals like calcium and magnesium. These minerals cause scale buildup in pipes and appliances. Ion exchange replaces these minerals with sodium or potassium ions. This makes water gentler on skin and clothes. It also protects water heaters and washing machines.
Industrial Applications
Industries need very pure water for their processes. Ion exchange removes metals, salts, and other contaminants. This protects equipment and improves product quality. Power plants use ion exchange to treat boiler water. Electronics factories rely on it to produce clean water. Food and beverage companies also use this method for safe water.
Wastewater Treatment
Ion exchange helps clean wastewater before release or reuse. It removes heavy metals like lead and mercury. It also reduces nitrates and other harmful chemicals. This process supports environmental safety by lowering pollution. Many treatment plants use ion exchange for better water management.

Credit: eaiwater.com
Comparing Ion Exchange To Other Methods
Different water treatment methods remove various contaminants. Ion exchange stands out for targeting specific ions. Comparing ion exchange with other common methods helps understand its benefits and limits. The focus here is on reverse osmosis and activated carbon, two popular alternatives.
Ion Exchange Vs. Reverse Osmosis
Ion exchange removes dissolved ions like calcium and magnesium. It softens hard water effectively. Reverse osmosis (RO) filters water through a membrane. RO removes a broad range of impurities, including salts, metals, and microbes.
Ion exchange uses resin beads to swap unwanted ions. RO pushes water through tiny pores, blocking many contaminants. Ion exchange does not remove bacteria or viruses. RO provides better microbial protection.
RO systems waste some water during filtration. Ion exchange uses less water overall. RO requires higher pressure and more energy. Ion exchange works well for hardness and specific mineral removal.
Ion Exchange Vs. Activated Carbon
Activated carbon filters remove chlorine, bad tastes, and odors. They trap organic compounds and some chemicals. Ion exchange targets dissolved minerals and metal ions. It does not remove chlorine or organic chemicals.
Activated carbon improves water flavor and smell. Ion exchange improves water hardness and metal content. Carbon filters need frequent replacement as they clog. Ion exchange resin can be regenerated and reused.
Both methods complement each other in water treatment. Carbon for taste and chemicals. Ion exchange for mineral balance and hardness.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Contaminants Does Ion Exchange Remove From Water?
Ion exchange removes heavy metals, calcium, magnesium, and some radioactive elements. It also reduces hardness and certain toxic ions, improving water quality.
How Effective Is Ion Exchange Against Hardness In Water?
Ion exchange is highly effective at softening water by replacing calcium and magnesium ions with sodium or potassium ions, reducing scale buildup.
Can Ion Exchange Remove Heavy Metals From Drinking Water?
Yes, ion exchange can remove heavy metals like lead, mercury, and cadmium by exchanging harmful ions with harmless ones, ensuring safer water.
Does Ion Exchange Eliminate Harmful Chemicals In Water?
Ion exchange primarily targets ions, so it removes some chemicals like nitrates and arsenic but may not remove all organic contaminants.
Conclusion
Ion exchange removes harmful minerals from water effectively. It targets calcium, magnesium, and heavy metals like lead. This process helps soften hard water and improve taste. Clean water supports better health and protects appliances. Choosing ion exchange means clearer, safer water at home.
Simple, reliable, and efficient—ion exchange is a smart solution. Clear water, easy living.

Hasan Al Sarker is a Reverse Osmosis Specialist. He has worked for many years to ensure safe drinking water for all. His research paper has been published in several journals, including Issue, Medium, and Slideshare. He is recognized as a water doctor among specialists though he did not attend medical college.
Besides working as a researcher of reverse osmosis technology, he is also very fancy with the kitchen and cooking. His guides are reading thousands of people every day. As a head of content, he is responsible for all the published articles at RO System Reviews.

