Have you ever wondered how water gets purified or how certain chemicals are separated in industries? The secret often lies in something called an ion exchanger.
Understanding what an ion exchanger is can help you see how it plays a crucial role in many everyday processes, from cleaning your drinking water to manufacturing medicines. If you want to know how this simple yet powerful tool works and why it matters to you, keep reading.
This article will break down the concept in easy terms and show you why ion exchangers are more important than you might think.

Credit: en.wikipedia.org
Ion Exchanger Basics
An ion exchanger is a material that swaps ions in a liquid. It helps remove unwanted ions and replace them with others. This process cleans water, purifies chemicals, and treats waste. Understanding ion exchanger basics helps grasp how this tool works in many industries.
Ion exchangers come in different types. Each type has unique features and uses. Knowing these types helps choose the right one for any task.
Types Of Ion Exchangers
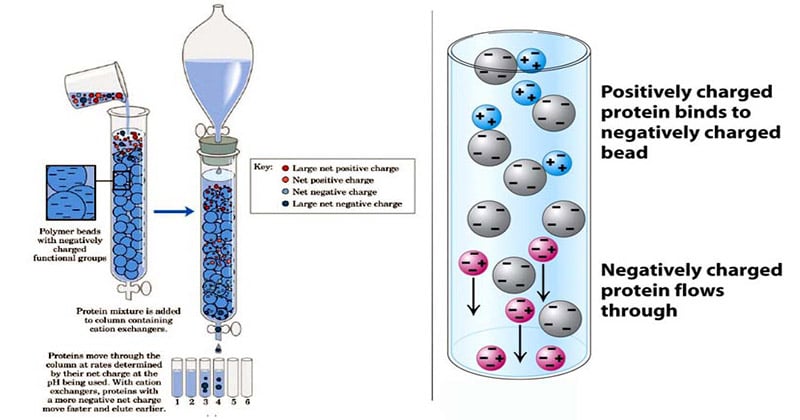
There are two main types of ion exchangers: cation and anion exchangers. Cation exchangers swap positive ions like calcium and magnesium. Anion exchangers replace negative ions like chloride and sulfate. Some exchangers combine both types. These mixed exchangers handle complex cleaning jobs.
How Ion Exchange Works
Ion exchange works by exchanging ions between a solution and the exchanger. The exchanger holds ions on its surface. When liquid passes through, unwanted ions trade places with the held ions. This keeps the liquid cleaner or changes its composition. The process repeats until the exchanger needs regeneration.
Key Materials Used
Ion exchangers use special materials with charged sites. Common materials include resins made from polymers. These resins have charged groups to attract ions. Natural materials like zeolites are also used. The choice of material depends on the specific ions to remove or replace.

Credit: www.britannica.com
Industrial Applications
Ion exchangers play a vital role across many industries. They help in removing unwanted ions from liquids and gases. This process improves product quality and safety. Ion exchangers also aid in recycling and reducing waste. They support efficient and eco-friendly operations.
Water Treatment
Ion exchangers remove hardness and impurities from water. They replace calcium and magnesium ions with sodium ions. This process softens water and prevents scale buildup. Water treatment plants use ion exchangers to provide clean drinking water. Industries rely on them to protect machines and pipes.
Chemical Processing
Chemical industries use ion exchangers for purification and separation. They isolate specific ions from mixtures. This improves the purity of raw materials and products. Ion exchangers help in recycling acids and bases. They also reduce waste and lower production costs.
Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
Pharmaceutical companies use ion exchangers to purify medicines and ingredients. They remove unwanted ions that affect drug quality. Ion exchangers ensure the safety and effectiveness of drugs. They also help maintain strict quality standards. This supports reliable and consistent pharmaceutical production.
Environmental Benefits
Ion exchangers play a key role in protecting the environment. They help reduce pollution, manage wastewater, and recover useful materials. These benefits support cleaner air, water, and soil. Understanding these advantages shows why ion exchangers matter for a healthier planet.
Pollution Control
Ion exchangers remove harmful ions from air and water. They capture toxic metals like lead and mercury. This stops pollutants from spreading in nature. Cleaner water and air mean safer ecosystems and healthier people. Ion exchangers help industries limit their pollution impact.
Wastewater Management
Industries produce wastewater full of contaminants. Ion exchangers treat this water by removing dangerous ions. This treatment makes water reusable and safe to release. It lowers water pollution and conserves fresh water. Using ion exchangers helps maintain water quality for communities and wildlife.
Resource Recovery
Ion exchangers recover valuable minerals and metals from waste. These materials include salt, copper, and rare earth elements. Recovering resources reduces the need for mining new materials. This saves energy and cuts environmental damage. It also supports recycling and sustainable use of resources.
Advantages Over Other Methods
Ion exchangers offer several benefits compared to other water treatment methods. They improve water quality efficiently and work well in many settings. Their unique features make them a preferred choice for removing unwanted ions.
Efficiency And Selectivity
Ion exchangers target specific ions in water. This selectivity helps remove contaminants precisely. The process works quickly and removes even low concentrations. It reduces the need for extra treatment steps. This saves time and effort during water purification.
Cost-effectiveness
Using ion exchangers lowers overall treatment costs. They consume less energy than many other methods. The materials used are durable and last long. This reduces replacement and maintenance expenses. The process also minimizes chemical use, cutting costs further.
Scalability
Ion exchangers adapt easily to different system sizes. They work well in small homes and large industries. The design can expand to meet growing water needs. This flexibility makes them useful in many applications. Users can upgrade without replacing the entire system.
Maintenance And Regeneration
Maintaining an ion exchanger is key to keeping it effective. Regular care helps it work longer and better. Regeneration restores its ability to swap ions properly. Both steps keep water clean and equipment safe.
Cleaning Procedures
Start by rinsing the ion exchanger with clean water. This removes dirt and debris inside the resin. Use a mild detergent if buildup occurs. Avoid harsh chemicals that can damage the resin beads. Clean the system parts connected to the exchanger too. Regular cleaning prevents clogs and reduces wear.
Regeneration Techniques
Regeneration uses special chemicals to refresh the resin. For cation exchangers, salt solutions are common. Anion exchangers often use acid or alkaline solutions. Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for the right amounts. Regenerate only when the exchanger loses efficiency. Proper regeneration extends the resin’s life.
Troubleshooting Common Issues
Check for low flow rates or poor water quality first. These signs may mean resin exhaustion or fouling. Clean or regenerate the exchanger to fix these problems. Look for cracks or leaks in the system parts. Replace damaged components quickly to avoid bigger issues. Regular checks help catch problems early.
Credit: microbenotes.com
Future Trends
The future of ion exchangers holds exciting possibilities. Advances in science and technology drive new developments. These improvements aim to make ion exchange more effective and eco-friendly. Industries will benefit from smarter, faster, and more durable ion exchangers.
Innovations In Materials
New materials improve ion exchange performance. Scientists create resins that last longer and work better. Some materials target specific ions, increasing precision. Nanotechnology helps produce smaller, more efficient particles. These changes reduce costs and improve results.
Emerging Applications
Ion exchangers find new uses beyond water treatment. They help in medicine, such as drug delivery systems. Food and beverage industries use ion exchangers for quality control. Environmental cleanup also benefits from advanced ion exchange methods. The range of applications keeps expanding rapidly.
Sustainability Focus
Eco-friendly ion exchangers become a priority. Researchers design reusable and biodegradable materials. Energy-efficient processes lower the carbon footprint. Waste from ion exchange is reduced and recycled. Sustainable practices help protect natural resources and reduce pollution.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is An Ion Exchanger Used For?
An ion exchanger removes unwanted ions from liquids. It purifies water, softens hard water, and treats industrial wastewater efficiently.
How Does An Ion Exchanger Work?
An ion exchanger swaps ions between a solution and a solid resin. This process removes contaminants and replaces them with harmless ions.
What Are Common Types Of Ion Exchangers?
The main types are cation exchangers and anion exchangers. Cation exchangers replace positive ions, while anion exchangers swap negative ions.
Where Are Ion Exchangers Commonly Applied?
Ion exchangers are used in water treatment, chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and food industries for purification and separation processes.
Conclusion
Ion exchangers help remove unwanted ions from water and other liquids. They work by swapping harmful ions with safer ones. This process improves water quality and makes it safer to use. Many industries and homes rely on ion exchangers every day.
Understanding how they work can help you appreciate their value. Simple, effective, and widely used—ion exchangers play a key role in clean water solutions.

Hasan Al Sarker is a Reverse Osmosis Specialist. He has worked for many years to ensure safe drinking water for all. His research paper has been published in several journals, including Issue, Medium, and Slideshare. He is recognized as a water doctor among specialists though he did not attend medical college.
Besides working as a researcher of reverse osmosis technology, he is also very fancy with the kitchen and cooking. His guides are reading thousands of people every day. As a head of content, he is responsible for all the published articles at RO System Reviews.

