Have you ever wondered how water gets purified or how certain chemicals are removed from your surroundings? The answer often lies in a simple yet powerful process called ion exchange.
Understanding what ion exchange is can help you see how this technique impacts your daily life—from clean drinking water to efficient industrial systems. By the time you finish this article, you’ll know exactly how ion exchange works and why it matters to you.
Ready to discover a process that quietly makes a big difference? Let’s dive in.
Credit: www.netsolwater.com
Basics Of Ion Exchange
Ion exchange is a process used to remove unwanted ions from liquids. It helps clean water and purify chemicals. The process swaps harmful ions with safe ones. This makes water softer or purer for use in homes and industries.
Understanding the basics of ion exchange is important. It explains how the process works and what materials are involved. This knowledge helps people see why ion exchange is useful and how it improves water quality.
How Ion Exchange Works
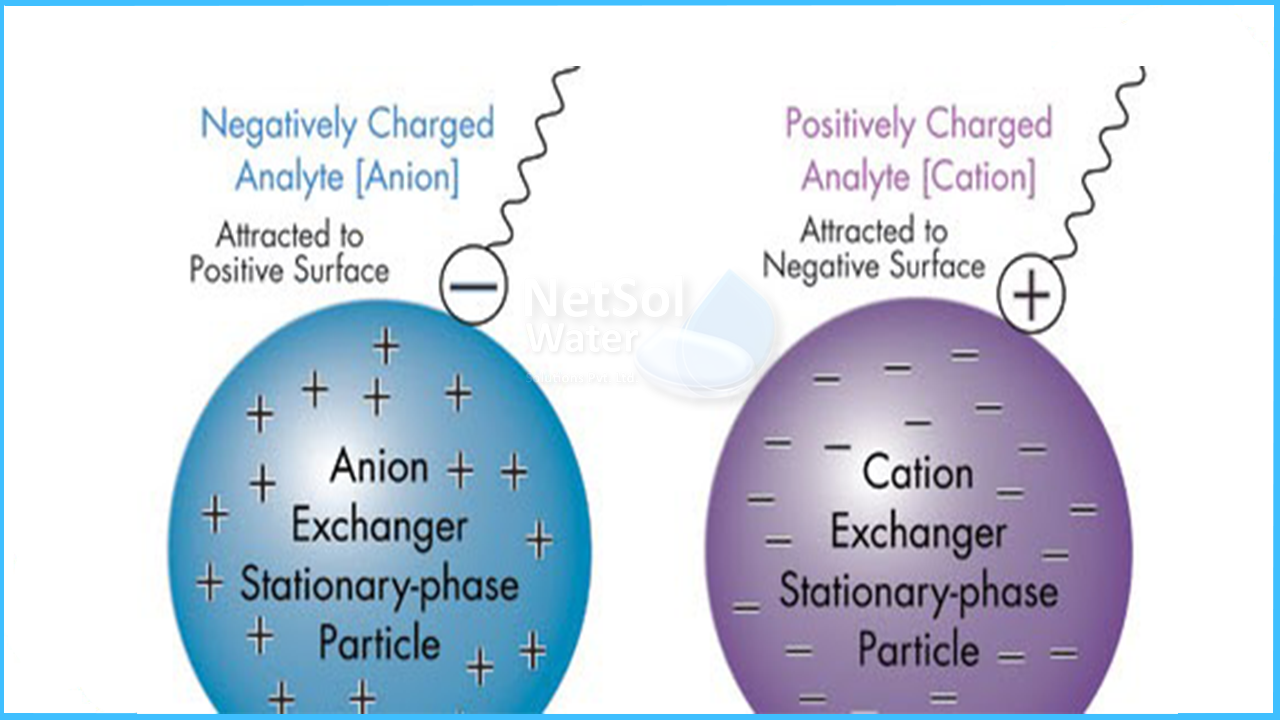
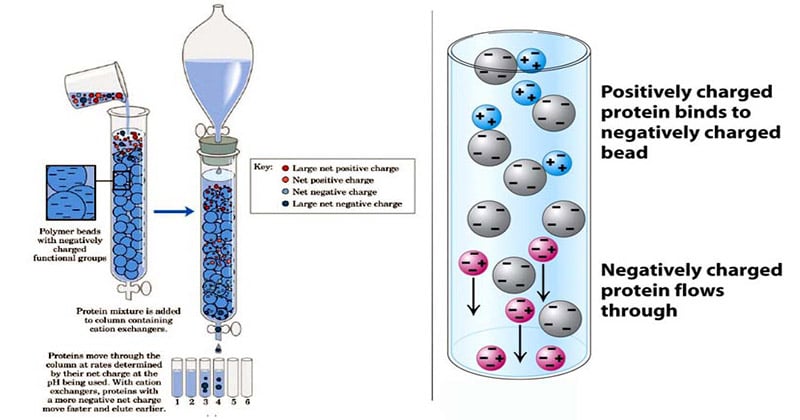
Ion exchange works by swapping ions between a liquid and a solid. The solid contains charged particles called resin beads. These beads attract and hold certain ions from the liquid. The unwanted ions are replaced by ions from the resin. This exchange cleans the liquid by removing harmful substances.
Types Of Ion Exchange Processes
There are two main types of ion exchange. Cation exchange swaps positively charged ions. Anion exchange swaps negatively charged ions. Some systems use both types together. This helps remove many different contaminants from water or solutions.
Common Ion Exchange Materials
The most common materials are ion exchange resins. These resins are made of small plastic beads. They carry positive or negative charges. Natural materials like zeolites and clays can also be used. Each material works best for certain ions and applications.
Key Benefits Of Ion Exchange
Ion exchange offers several key benefits across various fields. It plays a critical role in improving water quality, boosting industrial processes, and protecting the environment. The process is simple but effective, making it popular worldwide.
Water Purification Advantages
Ion exchange removes harmful minerals and contaminants from water. It softens hard water by replacing calcium and magnesium ions. This improves taste and reduces scale buildup in pipes and appliances. Clean water is essential for health and daily use.
Industrial Process Improvements
Industries use ion exchange to purify chemicals and separate materials. It helps produce high-quality products by removing impurities. The process also recovers valuable metals from waste streams. This increases efficiency and lowers production costs.
Environmental Impact Reduction
Ion exchange reduces waste by recycling water and materials. It lowers pollution by capturing harmful ions before release. This protects soil and water sources from contamination. The method supports sustainable practices in many industries.
Applications In Water Treatment
Ion exchange plays a key role in water treatment processes. It helps improve water quality by removing unwanted minerals and contaminants. This method uses special resins to swap harmful ions with safer ones. Below are some common applications of ion exchange in water treatment.
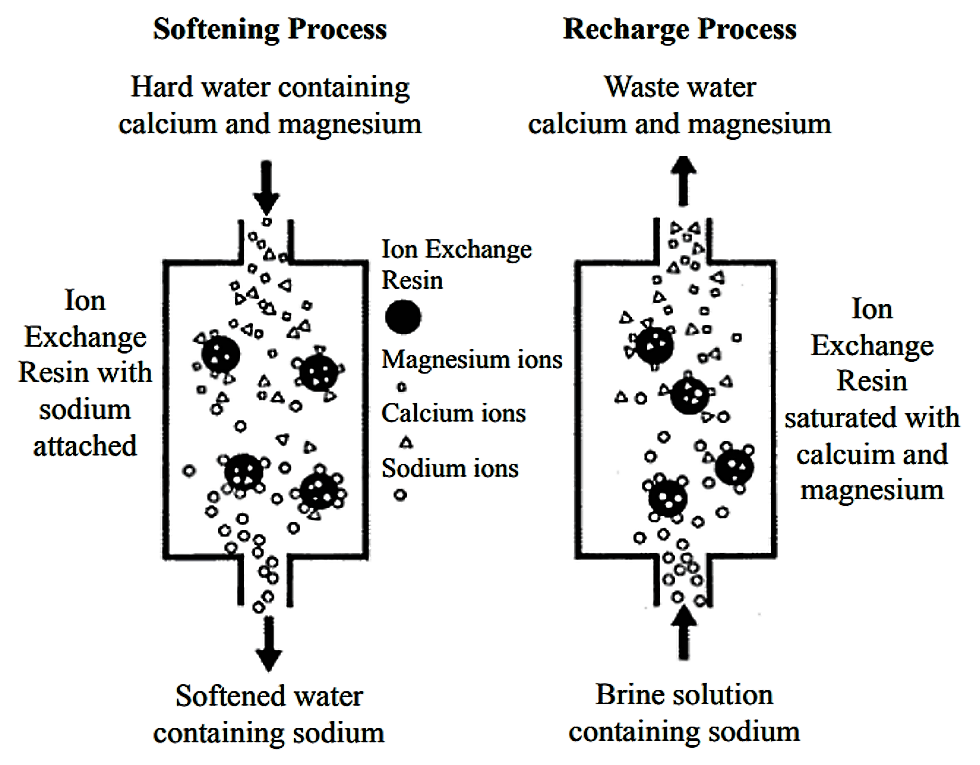
Softening Hard Water
Hard water contains calcium and magnesium ions that cause scale buildup. Ion exchange removes these ions and replaces them with sodium or potassium ions. This process prevents damage to pipes, appliances, and plumbing systems. Softened water also improves soap efficiency and leaves skin feeling smoother.
Removal Of Heavy Metals
Heavy metals like lead, mercury, and cadmium pose health risks in drinking water. Ion exchange resins attract and capture these toxic metals. This lowers their concentration to safe levels. The method is cost-effective and works well in both industrial and municipal water treatment plants.
Deionization And Demineralization
Deionization removes all charged particles from water, making it pure. Demineralization focuses on eliminating minerals such as salts. Ion exchange resins exchange unwanted ions with hydrogen and hydroxide ions. The result is highly purified water used in labs, pharmaceuticals, and electronics manufacturing.
Credit: sswm.info
Industrial Uses Of Ion Exchange
Ion exchange plays a crucial role in many industries. It helps remove unwanted ions and replaces them with useful ones. This process improves product quality and protects equipment. Industries rely on ion exchange for its efficiency and precision. Here are some main industrial uses of ion exchange.
Pharmaceutical Production
Ion exchange purifies raw materials in drug manufacturing. It removes harmful ions and impurities. This ensures medicines are safe and effective. It also controls the pH of solutions. Ion exchange helps in producing high-purity water. This water is essential for making many drugs. The process supports strict quality standards in pharma.
Food And Beverage Processing
Ion exchange improves taste and safety in food and drinks. It removes unwanted minerals and colors. This makes beverages clearer and better tasting. It also helps in sugar refining and juice clarification. Ion exchange controls the salt content in some foods. This method keeps products fresh and appealing.
Chemical Manufacturing
Ion exchange is key in chemical production. It purifies chemicals by removing impurities. This leads to better reactions and final products. It also recovers valuable materials from waste streams. Ion exchange protects machines from damage by hard water. It helps maintain smooth and efficient operations.
Emerging Technologies And Trends
Ion exchange technology is evolving with new innovations and trends. These changes improve efficiency, reduce costs, and make treatment safer. Emerging methods focus on better materials and combining techniques for stronger results. Sustainability is also a key focus, aiming to protect the environment while cleaning water and other substances.
Advanced Ion Exchange Resins
New ion exchange resins offer higher capacity and selectivity. These resins can target specific ions more accurately. They also last longer, reducing the need for frequent replacement. Improved resins work faster and handle tougher water conditions. This leads to better purification with less waste.
Hybrid Treatment Systems
Hybrid systems mix ion exchange with other treatment methods. Combining techniques enhances overall performance. For example, ion exchange paired with membrane filtration removes more contaminants. Hybrid systems can adapt to different water types and pollution levels. They provide flexible and effective treatment options.
Sustainability And Green Chemistry
Green chemistry principles guide new ion exchange developments. Using eco-friendly materials reduces environmental harm. Processes now focus on lowering energy use and waste production. Recycling and regenerating resins conserve resources. These advances help create cleaner water with a smaller footprint.
Credit: microbenotes.com
Maintenance And Challenges
Ion exchange systems need regular care to work well over time. Maintenance helps keep the system clean and efficient. It also prevents problems that could stop the system from working. Knowing the common challenges helps prepare for any issues. This way, the system lasts longer and stays reliable.
Regeneration Techniques
Regeneration restores the ion exchange resin’s ability to remove ions. This process uses chemicals like salt or acid. The resin releases trapped ions and gets fresh ions in return. Proper regeneration keeps the resin active and effective. Skipping this step can lower system performance quickly.
Common Operational Issues
Clogging and fouling happen when particles block the resin. Hard water minerals can build up and reduce flow. Resin beads may break or wear out with time. Poor regeneration can cause incomplete ion exchange. These problems reduce water quality and system efficiency.
Cost Considerations
Maintaining ion exchange systems costs money. Chemicals for regeneration add to the expense. Replacing worn resin can be costly. Energy use and water waste also affect the budget. Planning maintenance can help control these costs over time.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Ion Exchange In Water Treatment?
Ion exchange is a process that removes unwanted ions from water. It replaces harmful ions with harmless ones, improving water quality effectively.
How Does Ion Exchange Resin Work?
Ion exchange resin contains charged beads. These beads attract and swap ions in water, purifying it by removing contaminants like calcium or sodium.
What Are Common Uses Of Ion Exchange?
Ion exchange is used in water softening, purification, and chemical processing. It removes hardness, heavy metals, and other impurities from liquids efficiently.
What Ions Can Ion Exchange Remove?
Ion exchange can remove calcium, magnesium, sodium, and heavy metals. It targets charged particles, making water safer and cleaner for various uses.
Conclusion
Ion exchange is a simple and useful process. It helps remove unwanted ions from water and other solutions. Many industries use it to clean and soften water. This method is safe and cost-effective. Understanding ion exchange can help you see how water gets purified.
It plays a big role in daily life and industry. Learning about it makes you aware of water treatment methods. A small step toward cleaner water and better health.

Hasan Al Sarker is a Reverse Osmosis Specialist. He has worked for many years to ensure safe drinking water for all. His research paper has been published in several journals, including Issue, Medium, and Slideshare. He is recognized as a water doctor among specialists though he did not attend medical college.
Besides working as a researcher of reverse osmosis technology, he is also very fancy with the kitchen and cooking. His guides are reading thousands of people every day. As a head of content, he is responsible for all the published articles at RO System Reviews.

