Have you ever wondered how water gets purified or how certain chemicals are separated in industries? The answer often lies in a simple yet powerful method called the ion exchange process.
Understanding this process can help you grasp how clean water is made, how medicines are developed, and even how your home appliances stay protected. You’ll discover what ion exchange really is, why it matters to you, and how it works step by step.
By the end, you’ll see how this process quietly impacts your daily life in ways you might not have realized. Ready to uncover the secrets behind ion exchange? Let’s dive in.
Basics Of Ion Exchange
Understanding the basics of ion exchange helps explain how this process cleans and softens water. Ion exchange is a simple chemical method used in many water treatment systems. It removes unwanted ions and replaces them with useful ones. This process is important for industries, homes, and even laboratories.
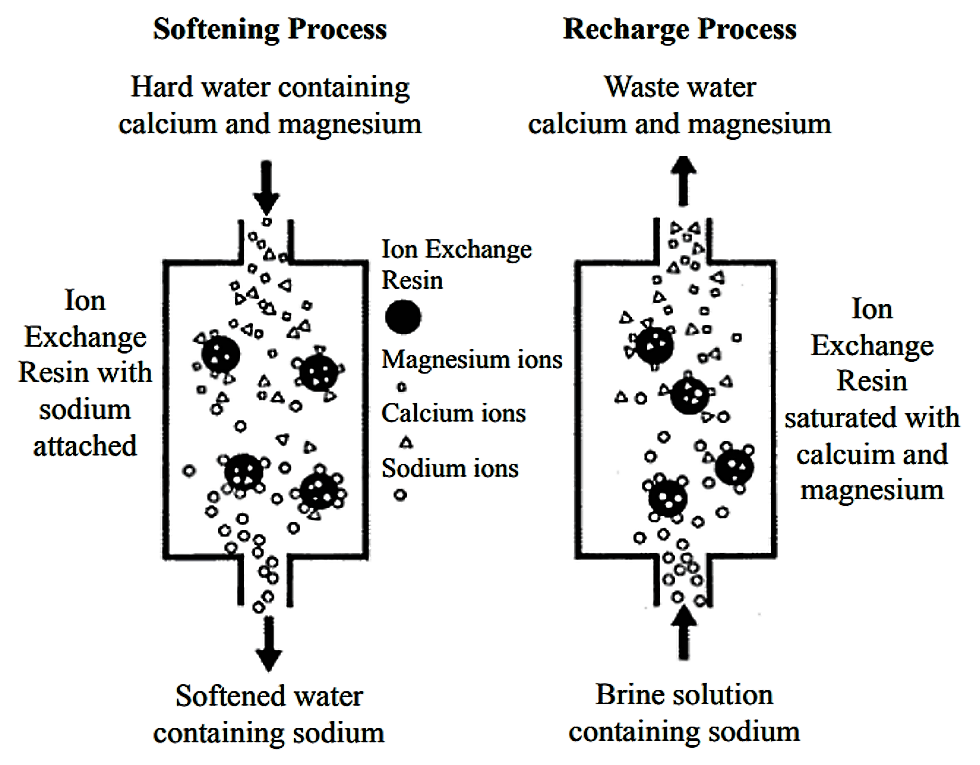
Ion exchange uses special materials called resins. These resins attract and hold ions from water. Then, they release other ions into the water. The result is purified or softened water that meets specific needs.
Ion Exchange Definition
Ion exchange is a process that swaps ions between a liquid and a solid. The solid is usually a resin with charged sites. These sites attract ions of the opposite charge from the liquid. As ions swap places, the water’s chemical makeup changes. This helps remove harmful substances or unwanted minerals.
How Ion Exchange Works
Water flows through a column filled with ion exchange resin. The resin holds ions it wants to remove. At the same time, it releases other ions into the water. This swap continues until the resin becomes full. Then, the resin can be cleaned and reused. The process is fast and effective for many water types.
Types Of Ion Exchange Resins
There are two main types of ion exchange resins: cation and anion. Cation resins swap positive ions like calcium and magnesium. Anion resins swap negative ions like chloride and sulfate. Some systems use both resins together for better water quality. Choosing the right resin depends on the water problem to solve.
Credit: sswm.info
Role In Water Purification
The ion exchange process plays a vital role in water purification. It helps remove unwanted substances and improves water quality. This method uses special resins to swap harmful ions with safer ones. The result is cleaner, safer water for daily use.
Removing Hardness From Water
Water hardness comes from calcium and magnesium ions. These ions cause scale buildup in pipes and appliances. Ion exchange replaces them with sodium or potassium ions. This softens the water and protects plumbing systems.
Eliminating Contaminants
Ion exchange removes heavy metals like lead and mercury. It also filters out nitrates and other harmful chemicals. The resins capture these contaminants and keep them out of drinking water. This makes water safer and healthier.
Improving Water Taste And Quality
Removing unwanted minerals improves water taste. Ion exchange reduces bitter or metallic flavors. It also lowers odors from chlorine and other chemicals. The process delivers fresh, clean water that tastes better.
Types Of Ion Exchange Processes
Ion exchange is a process that removes unwanted ions from liquids. It works by swapping ions in the liquid with ions on a solid material called resin. There are different types of ion exchange processes. Each type targets specific ions. Understanding these types helps in choosing the right method for water treatment or other uses.
Cation Exchange
Cation exchange removes positively charged ions from liquids. Common cations include calcium, magnesium, and sodium. The resin holds hydrogen or sodium ions. These ions swap places with unwanted cations in the liquid. This process helps soften hard water and remove heavy metals.
Anion Exchange
Anion exchange removes negatively charged ions. These include chloride, nitrate, and sulfate ions. The resin contains hydroxide or chloride ions. It exchanges these with harmful anions in the liquid. This method improves water quality by removing harmful acids and salts.
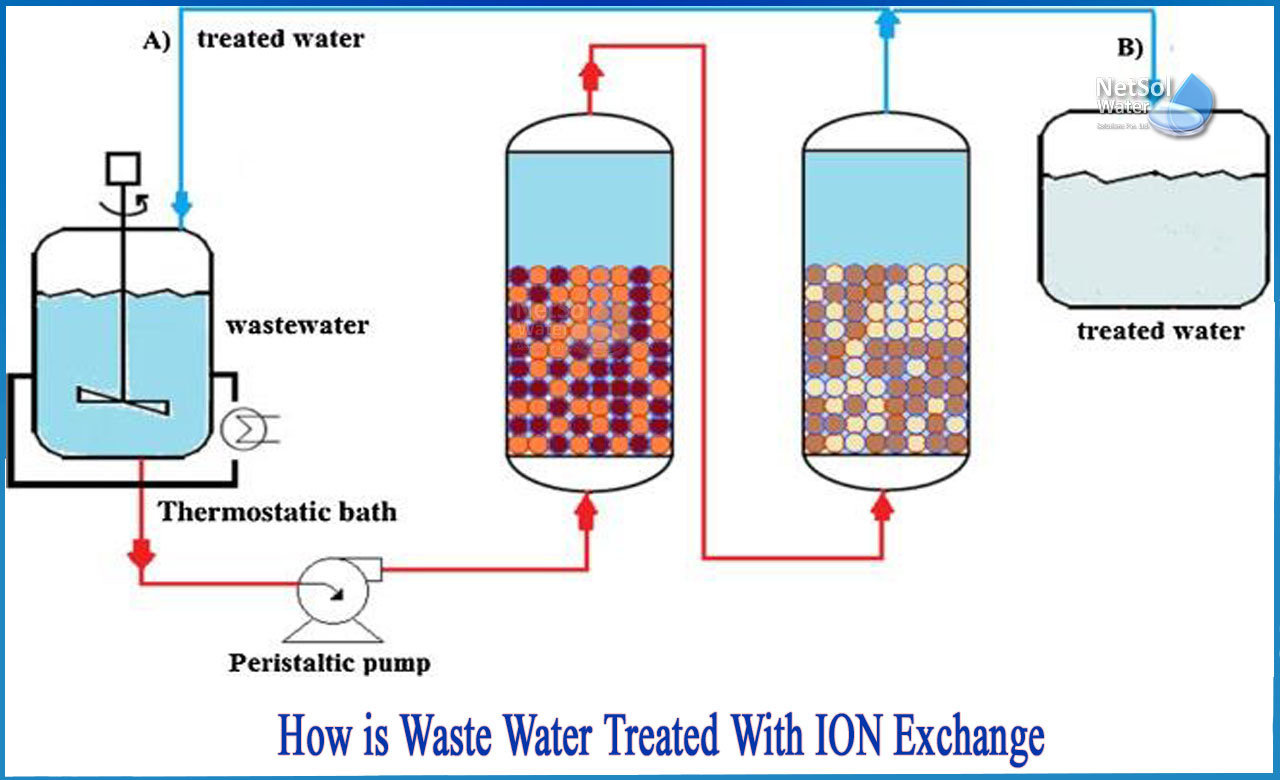
Mixed Bed Ion Exchange
Mixed bed combines both cation and anion resins. It removes both positive and negative ions simultaneously. This process produces very pure water. Mixed bed ion exchange is common in industries needing high purity water. It is often used after other treatments to polish the water.

Credit: textilelearner.net
Applications Of Ion Exchange
The ion exchange process finds many uses across different fields. It helps remove unwanted ions from liquids and replace them with useful ones. This method improves water quality and purifies chemicals. Its efficiency and simplicity make it popular in many industries.
Here are some common applications of ion exchange technology.
Residential Water Softeners
Ion exchange is key in home water softeners. It removes hard minerals like calcium and magnesium. These minerals cause scale buildup in pipes and appliances. The process swaps hard ions with sodium or potassium ions. This keeps water gentle and safe for daily use.
Industrial Water Treatment
Industries rely on ion exchange to treat large water volumes. It removes heavy metals, nitrates, and other harmful ions. Clean water helps prevent damage to machinery and products. It also meets strict environmental and safety standards. The process is cost-effective and reliable for factories.
Pharmaceutical And Food Industries
Ion exchange purifies chemicals in medicine and food production. It removes impurities that affect quality and safety. This process ensures products meet health regulations. It also helps recover valuable materials during manufacturing. Its precision is vital in these sensitive fields.
Advantages And Limitations
The ion exchange process offers many benefits but also comes with some limitations. Understanding both sides helps in choosing the right water treatment method. This section breaks down the main advantages and common challenges of ion exchange.
Benefits Of Ion Exchange
Ion exchange removes unwanted ions from water effectively. It improves water quality by softening hard water. The process can target specific ions, such as calcium and magnesium. It works well in industries and homes. Ion exchange systems are reusable after regeneration. They also operate without harmful chemicals. The process is fast and reliable for many applications.
Common Challenges
Ion exchange may not remove all contaminants. Some ions can reduce the resin’s lifespan. The process requires a steady water flow to work well. Resin beads can be sensitive to certain chemicals. Over time, resin can become clogged or fouled. The system needs proper care to avoid breakdowns. Initial setup costs can be higher than other methods.
Maintenance And Regeneration
Regular maintenance keeps ion exchange systems efficient. Resin beads need periodic regeneration with salt solutions. This step restores the resin’s ability to capture ions. Skipping regeneration lowers water quality and system life. Maintenance includes checking for leaks and resin condition. Proper regeneration reduces waste and saves costs. It ensures the system runs smoothly for a long time.
Future Trends In Ion Exchange
The ion exchange process is evolving with new trends shaping its future. These trends focus on improving efficiency, sustainability, and combining technologies. The goal is to make water treatment more effective and eco-friendly. Understanding these future trends helps us see how ion exchange will adapt to growing needs.
Advanced Resin Technologies
New resin materials improve ion exchange performance. These resins have higher capacity and faster ion removal. They resist fouling and last longer. Innovations include resins targeting specific contaminants. This makes treatment more precise and cost-effective. Advanced resins reduce waste and energy use.
Sustainable Water Treatment
Sustainability drives changes in ion exchange methods. Systems now focus on reducing chemical use and waste. Regeneration processes use less water and safer chemicals. Some designs recycle brine solutions to limit pollution. Sustainable ion exchange supports clean water goals worldwide. This trend helps protect natural resources.
Integration With Other Purification Methods
Ion exchange often combines with filtration and membrane technologies. This integration improves water quality and system efficiency. Hybrid systems remove a wider range of impurities. They can lower operating costs and energy needs. Combining methods creates flexible solutions for different water types. This approach meets stricter water standards.
Credit: www.netsolwater.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Ion Exchange Process Used For?
Ion exchange is used to remove unwanted ions from water. It purifies water by swapping harmful ions with harmless ones. This process is common in water softening and wastewater treatment.
How Does Ion Exchange Work In Water Treatment?
Ion exchange works by exchanging ions between a solution and a resin. The resin captures unwanted ions and releases beneficial ones. This improves water quality by removing hardness and contaminants.
What Materials Are Used In Ion Exchange Resins?
Ion exchange resins are typically made of synthetic polymers. They contain charged groups that attract specific ions. Common types include cation and anion exchange resins.
Is Ion Exchange Process Environmentally Friendly?
Yes, ion exchange is eco-friendly as it uses recyclable resins. It reduces chemical waste compared to other purification methods. Proper resin regeneration minimizes environmental impact.
Conclusion
The ion exchange process helps remove unwanted ions from water. It uses special resins to swap harmful particles with safer ones. This method cleans water for homes and industries. It also helps in softening hard water. The process is simple, effective, and widely used.
Understanding it makes water treatment clearer. Clean water means better health and safer use. Ion exchange plays a key role in daily life. A small step for cleaner water, a big step for us all.

Hasan Al Sarker is a Reverse Osmosis Specialist. He has worked for many years to ensure safe drinking water for all. His research paper has been published in several journals, including Issue, Medium, and Slideshare. He is recognized as a water doctor among specialists though he did not attend medical college.
Besides working as a researcher of reverse osmosis technology, he is also very fancy with the kitchen and cooking. His guides are reading thousands of people every day. As a head of content, he is responsible for all the published articles at RO System Reviews.

